A) heat does not involve a transfer of energy.
B) cells do not have much heat; they are relatively cool.
C) temperature is usually uniform throughout a cell.
D) heat can never be used to do work.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in Figure 6.4. 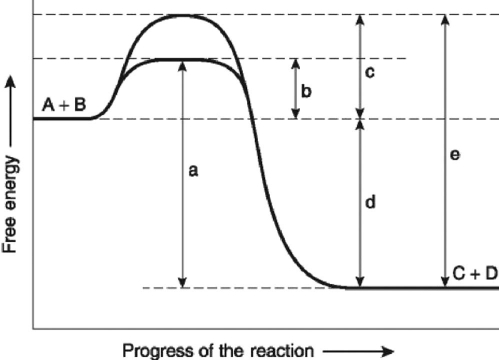 Figure 6.4
-Which of the following represents the ΔG of the reaction in Figure 6.4?
Figure 6.4
-Which of the following represents the ΔG of the reaction in Figure 6.4?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In experimental tests of enzyme evolution, a gene encoding an enzyme was subjected to multiple cycles of random mutagenesis and selection for altered substrate specificity. The resulting enzyme had altered substrate specificity and multiple amino acid changes. Where in the enzyme would you expect these amino acid changes to be located?
A) only in or near the active site
B) only in the hydrophobic interior of the folded protein
C) only at surface sites distant from the active site
D) in or near the active site and at surface sites distant from the active site
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question(s) are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in Figure 6.4.  Figure 6.4
-Which of the following best describes the forward reaction in Figure 6.4?
Figure 6.4
-Which of the following best describes the forward reaction in Figure 6.4?
A) endergonic, ∆G > 0
B) exergonic, ∆G < 0
C) endergonic, ∆G < 0
D) exergonic, ∆G > 0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some bacteria are metabolically active in hot springs because
A) they are able to maintain a lower internal temperature.
B) high temperatures make catalysis unnecessary.
C) their enzymes have high optimal temperatures.
D) their enzymes are completely insensitive to temperature.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A chemical reaction that has a positive ΔG is best described as
A) endergonic.
B) entropic
C) spontaneous.
D) exergonic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
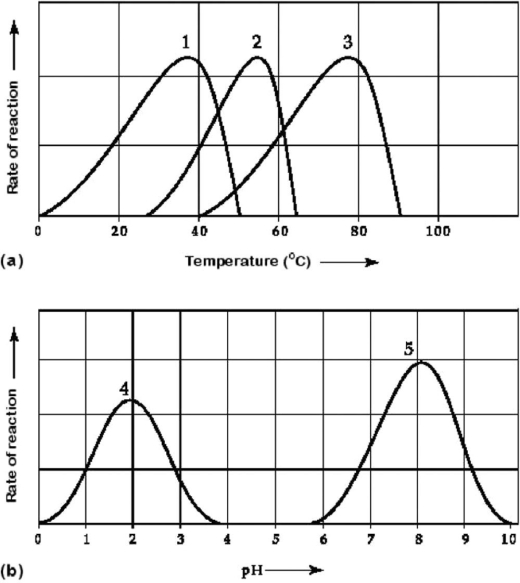 Figure 6.3 Activity of various enzymes (a) at various temperatures and (b) at various pH.
-Which temperature and pH profile curves on the graphs in Figure 6.3 were most likely generated from analysis of an enzyme from a human stomach, where conditions are strongly acid?
Figure 6.3 Activity of various enzymes (a) at various temperatures and (b) at various pH.
-Which temperature and pH profile curves on the graphs in Figure 6.3 were most likely generated from analysis of an enzyme from a human stomach, where conditions are strongly acid?
A) curves 1 and 4
B) curves 1 and 5
C) curves 2 and 4
D) curves 2 and 5
E) curves 3 and 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
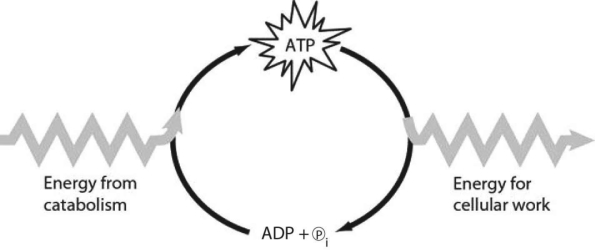 Figure 6.1
-Which of the following is the most correct interpretation of Figure 6.1?
Figure 6.1
-Which of the following is the most correct interpretation of Figure 6.1?
A) Inorganic phosphate is created from organic phosphate.
B) Energy from catabolism can be used directly for performing cellular work.
C) ADP + ℗i are a set of molecules that store energy for catabolism.
D) ATP is a molecule that acts as an intermediary to store energy for cellular work.
E) ℗i acts as a shuttle molecule to move energy from ATP to ADP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. Succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to fumarate. The reaction is inhibited by malonic acid, which resembles succinate but cannot be acted upon by succinate dehydrogenase. Increasing the ratio of succinate to malonic acid reduces the inhibitory effect of malonic acid. -What is the role of malonic acid with respect to succinate dehydrogenase?
A) It is a noncompetitive inhibitor.
B) It is a competitive inhibitor.
C) It blocks the binding of fumarate.
D) It is an allosteric regulator.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following metabolic processes can occur without a net influx of energy from some other process?
A) ADP + <IMG/>i → ATP + H₂O
B) C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ → 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O
C) 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂
D) amino acids → protein
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the difference (if any) between the structure of ATP and the structure of the precursor of the A nucleotide in RNA?
A) The sugar molecule is different.
B) The nitrogen-containing base is different.
C) The number of phosphates is three instead of one.
D) The number of phosphates is three instead of two.
E) There is no difference.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under a particular set of conditions in the lab, the enzyme in a chemical reaction is saturated. Which of the following alterations to the reaction will increase the rate at which substrate is converted to product?
A) increasing the concentration of substrate in the reaction
B) increasing the amount of enzyme in the reaction
C) increasing the volume of the reaction without increasing the amount of substrate or enzyme
D) decreasing the concentration of product in the reaction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate, the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products is to
A) add more of the enzyme.
B) heat the solution to 90°C.
C) add more substrate.
D) add an allosteric inhibitor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the question(s) below. Succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to fumarate. The reaction is inhibited by malonic acid, which resembles succinate but cannot be acted upon by succinate dehydrogenase. Increasing the ratio of succinate to malonic acid reduces the inhibitory effect of malonic acid. -Based on this information, which of the following is correct?
A) Succinate dehydrogenase is the enzyme, and fumarate is the substrate.
B) Succinate dehydrogenase is the enzyme, and malonic acid is the substrate.
C) Succinate is the substrate, and fumarate is the product.
D) Fumarate is the product, and malonic acid is a noncompetitive inhibitor.
E) Malonic acid is the product, and fumarate is a competitive inhibitor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
ATP hydrolysis in a test tube releases only about half as much energy as ATP hydrolysis in the cell. Which of the following is the best explanation for this observation?
A) Cells maintain higher internal pressure, which speeds up the reaction rate.
B) ATP hydrolysis in a test tube occurs under standard conditions; in the cell, reactant and product concentrations differ from standard conditions.
C) ATP hydrolysis in a cell produces different products than ATP hydrolysis in a test tube.
D) ATP hydrolysis in cells is catalyzed by enzymes, which releases more energy than the uncatalyzed reaction in a test tube.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemical equilibrium is relatively rare in living cells. Which of the following could be an example of a reaction at chemical equilibrium in a cell?
A) a chemical reaction in which the free energy at equilibrium is higher than the free-energy content at any point away from equilibrium
B) a chemical reaction in which neither the reactants nor the products are being produced or used in any other active metabolic pathway at that time in the cell
C) an endergonic reaction in an active metabolic pathway in which the energy for that reaction is supplied only by heat from the environment
D) Chemical equilibrium is not possible under any circumstances in a living cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about enzyme-catalyzed reactions is true?
A) The free-energy change of the reaction is greater than when the same reaction occurs in the absence of an enzyme.
B) The rate of the reaction is greater than when the same reaction occurs in the absence of an enzyme.
C) Enzymes always drive reactions toward chemical equilibrium.
D) Energy from ATP is required to activate the enzyme before it can catalyze the reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alteration of an amino acid at a site distant from the active site of an enzyme may alter the substrate specificity of the enzyme by
A) changing the optimum pH for the enzyme.
B) changing the intracellular location of the enzyme.
C) changing the binding site for an allosteric regulator.
D) changing the conformation of the enzyme.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + ℗i, the free-energy change is -7.3 kcal/mol under standard conditions (1 M concentration of both reactants and products) . In the cellular environment, however, the free-energy change is about -13 kcal/mol. What can we conclude about the free-energy change for the formation of ATP from ADP and ℗i under cellular conditions?
A) It is +7.3 kcal/mol.
B) It is less than +7.3 kcal/mol.
C) It is about +13 kcal/mol.
D) It is about +26 kcal/mol.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The induced fit model of enzyme activity suggests which of the following?
A) The binding of substrate depends on the conformation of the active site.
B) The binding of an activator alter the conformation of the active site to bind products more tightly.
C) The binding of substrate changes the conformation of the active site to bind substrate more tightly.
D) The binding of a competitive inhibitor changes the shape of the active site to bind substrate less tightly.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 79
Related Exams