A) tortoiseshell females; tortoiseshell males
B) black females; orange males
C) orange females; orange males
D) tortoiseshell females; black males
E) orange females; black males
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At what point in cell division is a chromosome lost so that, after fertilization with a normal gamete, the result is an embryo with 45, X? I. an error in anaphase I II) an error in anaphase II III) an error of the first postfertilization mitosis IV) an error in pairing
A) I or II only
B) II or IV only
C) III or IV only
D) I, II, or III only
E) I, II, III, or IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Normally, only female cats have the tortoiseshell phenotype because
A) the males die during embryonic development.
B) a male inherits only one allele of the X-linked gene controlling hair color.
C) the Y chromosome has a gene blocking orange coloration.
D) only males can have Barr bodies.
E) multiple crossovers on the Y chromosome prevent orange pigment production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Recombination between linked genes comes about for what reason?
A) Mutation on one homolog is different from that on the other homolog.
B) Independent assortment sometimes fails because Mendel had not calculated appropriately.
C) When genes are linked they always "travel" together at anaphase.
D) Crossovers between these genes result in chromosomal exchange.
E) Nonrecombinant chromosomes break and then re-join with one another.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
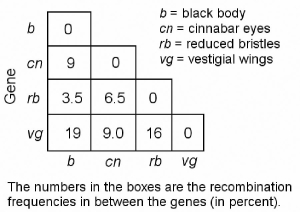 Figure 12.2
-In a series of mapping experiments, the recombination frequencies for four different linked genes of Drosophila were determined as shown in Figure 12.2. What is the order of these genes on a chromosome map?
Figure 12.2
-In a series of mapping experiments, the recombination frequencies for four different linked genes of Drosophila were determined as shown in Figure 12.2. What is the order of these genes on a chromosome map?
A) rb-cn-vg-b
B) vg-b-rb-cn
C) cn-rb-b-vg
D) b-rb-cn-vg
E) vg-cn-b-rb
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 12.1 shows a map of four genes on a chromosome.
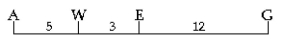 Figure 12.1
-Between which two genes would you expect the highest frequency of recombination?
Figure 12.1
-Between which two genes would you expect the highest frequency of recombination?
A) A and W
B) W and E
C) E and G
D) A and E
E) A and G
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Map units on a linkage map cannot be relied upon to calculate physical distances on a chromosome for which of the following reasons?
A) The frequency of crossing over varies along the length of the chromosome.
B) The relationship between recombination frequency and map units is different in every individual.
C) Physical distances between genes change during the course of the cell cycle.
D) The gene order on the chromosomes is slightly different in every individual.
E) Linkage map distances are identical between males and females.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the greatest benefit of having used a testcross for this experiment?
A) The homozygous recessive parents are obvious to the naked eye.
B) The homozygous parents are the only ones whose crossovers make a difference.
C) Progeny can be scored by their phenotypes alone.
D) All of the progeny will be heterozygous.
E) The homozygous recessive parents will be unable to cross over.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A phenotypically normal prospective couple seeks genetic counseling because the man knows that he has a translocation of a portion of his chromosome 4 that has been exchanged with a portion of his chromosome 12. Although he is normal because his translocation is balanced, he and his wife want to know the probability that his sperm will be abnormal. What is your prognosis regarding his sperm?
A) One-fourth will be normal, 1/4 will have the translocation, and 1/2 will have duplications and deletions.
B) All will carry the same translocation as the father.
C) None will carry the translocation because abnormal sperm will die.
D) His sperm will be sterile and the couple might consider adoption.
E) One-half will be normal and the rest will have the father's translocation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sex determination in mammals is due to the SRY region of the Y chromosome. An abnormality of this region could allow which of the following to have a male phenotype?
A) Turner syndrome, 45, X
B) translocation of SRY to an autosome of a 46, XX individual
C) a person with an extra X chromosome
D) a person with one normal and one shortened (deleted) X
E) Down syndrome, 46, XX
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the reason that closely linked genes are typically inherited together?
A) The likelihood of a crossover event between these two genes is low.
B) The number of genes in a cell is greater than the number of chromosomes.
C) Chromosomes are unbreakable.
D) Alleles are paired together during meiosis.
E) Genes align that way during metaphase I of meiosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The greatest distance among the three genes is between a and c. What does this mean?
A) Gene c is between a and b.
B) Genes are in the order: a-b-c.
C) Gene a is not recombining with c.
D) Gene a is between b and c.
E) Distance a-b is equal to distance a-c.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Abnormal chromosomes are frequently found in malignant tumors. Errors such as translocations may place a gene in close proximity to different control regions. Which of the following might then occur to make the cancer worse?
A) an increase in nondisjunction
B) expression of inappropriate gene products
C) a decrease in mitotic frequency
D) death of the cancer cells in the tumor
E) sensitivity of the immune system
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the explanation for this result?
A) The gene involved is on the Y chromosome.
B) The gene involved is on the X chromosome.
C) The gene involved is on an autosome, but only in males.
D) Other male-specific factors influence eye color in flies.
E) Other female-specific factors influence eye color in flies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does a frequency of recombination of 50% indicate?
A) The two genes are likely to be located on different chromosomes.
B) All of the offspring have combinations of traits that match one of the two parents.
C) The genes are located on sex chromosomes.
D) Abnormal meiosis has occurred.
E) Independent assortment is hindered.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
They have a daughter who is a dwarf with normal color vision. What is the probability that she is heterozygous for both genes?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A couple has a child with Down syndrome. The mother is 39 years old at the time of delivery. Which of the following is the most probable cause of the child's condition?
A) The woman inherited this tendency from her parents.
B) One member of the couple carried a translocation.
C) One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in somatic cell production.
D) One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in gamete production.
E) The mother had a chromosomal duplication.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true of linkage?
A) The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them.
B) The observed frequency of recombination of two genes that are far apart from each other has a maximum value of 100%.
C) All of the traits that Mendel studied-seed color, pod shape, flower color, and others-are due to genes linked on the same chromosome.
D) Linked genes are found on different chromosomes.
E) Crossing over occurs during prophase II of meiosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of aneuploidies in general?
A) A monosomy is more frequent than a trisomy.
B) 45, X is the only known human live-born monosomy.
C) Some human aneuploidies have selective advantage in some environments.
D) Of all human aneuploidies, only Down syndrome is associated with mental retardation.
E) An aneuploidy resulting in the deletion of a chromosome segment is less serious than a duplication.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If recombination frequency is equal to distance in map units, what is the approximate distance between genes A and B?
A) 1.5 map units
B) 3 map units
C) 6 map units
D) 15 map units
E) 30 map units
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 46
Related Exams