A) competitive inhibition.
B) noncompetitive inhibition.
C) feedback inhibition.
D) irreversible inhibition.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How do fatty acids travel through a cell membrane?
A) diffusion
B) active transport
C) carrier proteins
D) endocytosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is true about the data in the accompanying figure? 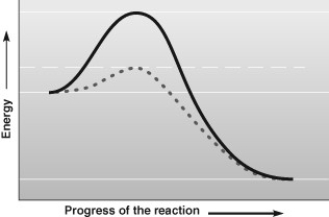
A) The solid line represents a reaction that has been catalyzed by an enzyme.
B) The dashed line represents a reaction that includes an enzyme and a cofactor.
C) Both lines represent endergonic reactions.
D) The energy of the products is higher than the energy of the reactants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inhibition of an enzyme is irreversible when
A) a competitive inhibitor is involved.
B) a noncompetitive inhibitor is involved.
C) there is an abundance of substrate.
D) covalent bonds form between inhibitor and enzyme.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cells acquire low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) by
A) diffusion.
B) receptor-mediated endocytosis.
C) exocytosis.
D) phagocytosis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding diffusion is false?
A) Diffusion is a result of the thermal energy of atoms and molecules.
B) Diffusion requires no input of energy into the system.
C) Diffusion occurs when particles spread from areas where they are less concentrated to areas where they are more concentrated.
D) Diffusion occurs even after equilibrium is reached and no net change is apparent.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Osmosis can be defined as
A) the diffusion of water.
B) the diffusion of nonpolar molecules.
C) active transport.
D) the diffusion of a solute.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the basic difference between exergonic and endergonic reactions?
A) Exergonic reactions involve ionic bonds; endergonic reactions involve covalent bonds.
B) Exergonic reactions involve the breaking of bonds; endergonic reactions involve the formation of bonds.
C) Exergonic reactions release energy; endergonic reactions absorb it.
D) In exergonic reactions, the reactants have less chemical energy than the products; in endergonic reactions, the opposite is true.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Aquaporins
A) allow water to cross the plasma membrane via facilitated diffusion.
B) allow water to cross the plasma membrane against its concentration gradient.
C) allow for the active transport of water.
D) are found in all cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the lab, you use a special balloon that is permeable to water but not sucrose to make an "artificial cell." The balloon is filled with a solution of 20% sucrose and 80% water and is immersed in a beaker containing a solution of 40% sucrose and 60% water. The solution in the balloon is ________ relative to the solution in the beaker.
A) isotonic
B) hypotonic
C) hypertonic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Water movement is important in urine formation in the kidneys. Urine is formed when the blood is filtered by the kidneys into kidney tubules. Three figures are presented here that relate to how the kidney tubules respond to the administration of the hormone vasopressin. The direction that water flows in these figures is from the kidney tubules back into the blood.
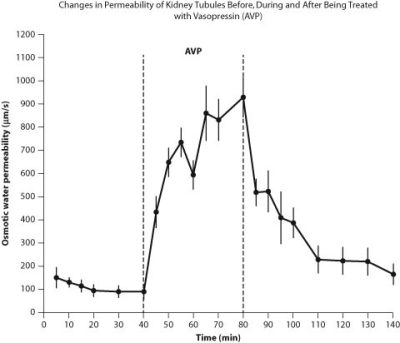 Figure A. Changes in permeability of tubules in the kidney in response to the hormone vasopressin (AVP) , which aids in osmoregulation.
Figure A. Changes in permeability of tubules in the kidney in response to the hormone vasopressin (AVP) , which aids in osmoregulation.
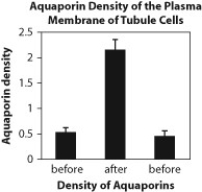 Figure B. Density of aquaporins in kidney tubule cells before, during, and after administration of vasopressin.
Figure B. Density of aquaporins in kidney tubule cells before, during, and after administration of vasopressin.
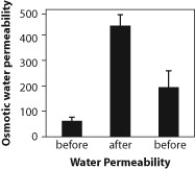 Figure C. Permeability of tissues to water before, during, and after administration of vasopressin.
-Based on the data from these figures, what do you expect the urine of a person to be like when vasopressin is having an effect on the kidney tubules?
Figure C. Permeability of tissues to water before, during, and after administration of vasopressin.
-Based on the data from these figures, what do you expect the urine of a person to be like when vasopressin is having an effect on the kidney tubules?
A) The urine will be salty.
B) The urine will be dilute.
C) The urine will be concentrated.
D) There will be large volumes of urine.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which figure depicts an animal cell placed in a solution hypotonic to the cell? 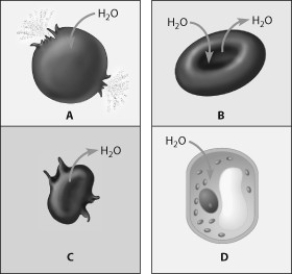
A) cell A
B) cell B
C) cell C
D) cell D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes is classified as a metabolic pathway?
A) the synthesis of a protein
B) water moving across a membrane via osmosis
C) the death and lysis of a cell
D) the movement of oxygen across a membrane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A man with a dirty cut on his hand appears at the emergency department for treatment. In order to clean the wound, the health-care provider should use
A) a solution of very low pH.
B) a solution of sterilized tap water.
C) a weak (low concentration) solution of salt water.
D) distilled water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If placed in tap water, an animal cell will undergo lysis, whereas a plant cell will not. What accounts for this difference?
A) the expulsion of water by the plant cell's central vacuole
B) the relative impermeability of the plant cell wall to water
C) the fact that plant cells are isotonic to tap water
D) the relative inelasticity and strength of the plant cell wall
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the lab, you use a special balloon that is permeable to water but not sucrose to make an "artificial cell." The balloon is filled with a solution of 20% sucrose and 80% water and is immersed in a beaker containing a solution of 40% sucrose and 60% water. Which of the following will occur?
A) Water will leave the balloon.
B) Water will enter the balloon.
C) Sucrose will leave the balloon.
D) Sucrose will enter the balloon.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Certain cells that line the stomach synthesize a digestive enzyme and secrete it into the stomach. This enzyme is a protein. Which of the following processes could be responsible for its secretion?
A) receptor-mediated endocytosis
B) exocytosis
C) diffusion
D) phagocytosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding active transport is false?
A) Active transport uses ATP as an energy source.
B) Active transport can move a solute against its concentration gradient.
C) Active transport requires the cell to expend energy.
D) Active transport is driven by the concentration gradient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following substances could be a cofactor?
A) a protein
B) a polypeptide
C) a zinc atom
D) a ribosome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The transfer of a phosphate group to a molecule or compound is called
A) carboxylation.
B) ionization.
C) phosphorylation.
D) hydrogenation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 81
Related Exams