A) matter in food is turned into energy in ATP.
B) energy in food is transferred to energy in ATP.
C) matter in ATP is used to fuel biosynthesis.
D) energy in food becomes matter in forming new molecules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conversion of CO2 and H2O into organic compounds using energy from light is called
A) glycolysis.
B) photosynthesis.
C) fermentation.
D) cellular respiration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The overall equation for the cellular respiration of glucose is
A) C5H12O6 + 6 O2 → 5 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy.
B) 5 CO2 + 6 H2O → C5H12O6 + 6 O2 + energy.
C) C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + energy.
D) C6H12O6 + energy → 6 CO2+ 6 H2O + 6 O2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which of the following phases of cellular respiration does substrate-level phosphorylation take place?
A) glycolysis only
B) the citric acid cycle only
C) oxidative phosphorylation only
D) glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A kilocalorie is defined as
A) the quantity of glucose needed to increase the body temperature by 1°C.
B) the quantity of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C.
C) the quantity of food used to maintain normal bodily functions.
D) the quantity of food consumed during a given type of exercise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A student studying bird development recorded the mass of eggs from the time they were laid until the time they hatched in order to relate the mass of the egg to the final mass of the chick.
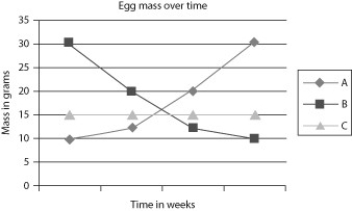 -Which of these lines represents the pattern of change in mass over that time?
-Which of these lines represents the pattern of change in mass over that time?
A) A
B) B
C) C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes produces the most ATP per molecule of glucose oxidized?
A) aerobic respiration
B) alcoholic fermentation
C) lactic acid fermentation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the electron transport chain, the final electron acceptor is
A) oxygen
B) carbon dioxide.
C) water.
D) ADP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bacteria that are unable to survive in the presence of oxygen are called
A) obligate anaerobes.
B) obligate aerobes.
C) facultative anaerobes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Food provides
A) raw materials for biosynthesis only.
B) energy for cell activities only.
C) raw materials for biosynthesis and energy for cell activities.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding photosynthesis and cellular respiration is true?
A) Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts, and cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria.
B) Photosynthesis occurs in mitochondria, and cellular respiration occurs in chloroplasts.
C) Photosynthesis occurs in mitochondria and in chloroplasts.
D) Cellular respiration occurs in mitochondria and in chloroplasts.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The end products of glycolysis include
A) NADH.
B) acetyl CoA.
C) citric acid.
D) O2.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During cellular respiration, NADH
A) is chemically converted into ATP.
B) is reduced to form NAD+.
C) delivers its electron load to the first electron carrier molecule.
D) is the final electron acceptor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the energy yields from cellular respiration is true?
A) Cellular respiration is more efficient at harnessing energy from glucose than car engines are at harnessing energy from gasoline.
B) Cellular respiration converts all of the energy in glucose into energy in ATP.
C) Cellular respiration converts the kinetic energy of glucose into chemical energy.
D) The heat produced during cellular respiration is only a tiny fraction of the chemical energy available in a glucose molecule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As a result of glycolysis, there is a net gain of ________ ATP(s) .
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 36
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The mitochondrial cristae are an adaptation that
A) permits the expansion of mitochondria as oxygen accumulates in the mitochondrial matrix.
B) helps mitochondria divide during times of greatest cellular respiration.
C) increases the space for more copies of the electron transport chain and ATP synthase complexes.
D) carefully encloses the DNA housed within the mitochondrial matrix.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNP is a chemical that has been used by people to lose weight. However, it is a dangerous option and has caused several people to die. DNP works in a fashion similar to that of brown fat. Based on this information, how would DNP cause weight loss and death?
A) DNP must prevent food from being consumed aerobically, so cells instead perform fermentation, and lactate buildup is deadly.
B) DNP must increase the rate of substrate-level phosphorylation, causing NADH to be produced more quickly than it can be used by the electron transport chain.
C) DNP must block cells from using fats and proteins to make ATP.
D) DNP must increase metabolism of food by producing heat instead of ATP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most bats are inactive during the day (this is known as torpor) and feed during the night. The graph below shows hypothetical data for a bat species.
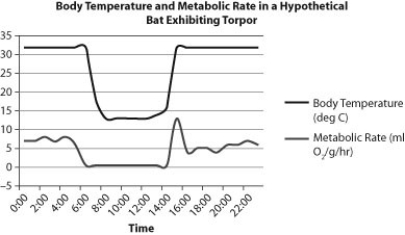 -Based on this graph, what is the relationship between metabolic rate and body temperature?
-Based on this graph, what is the relationship between metabolic rate and body temperature?
A) When metabolic rate drops, so does body temperature.
B) When metabolic rate drops, body temperature rises.
C) When metabolic rate drops, body temperature remains constant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Pasteur effect shows that yeasts consume glucose at a higher rate under anaerobic conditions than under aerobic conditions. Which of the following statements correctly explains this observation?
A) Yeasts are obligate anaerobes, so aerobic conditions will kill yeasts.
B) Yeasts are photosynthetic, so they are able to produce their own oxygen.
C) Less ATP is made under anaerobic conditions, so more glucose must be consumed to produce an equivalent amount of ATP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding food is false?
A) Food provides the raw materials for biosynthetic pathways that make molecules for cellular repair and growth.
B) Food provides the raw materials for biosynthetic pathways that can produce molecules that are not actually present in the original food.
C) Food provides the raw materials for biosynthetic pathways that can produce sugar by a process that is the exact opposite of glycolysis.
D) Food provides the raw materials for biosynthetic pathways that consume ATP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 82
Related Exams