A) will consistently produce more than the efficient quantity of the good.
B) will produce an efficient quantity of the good.
C) will consistently produce less than the efficient quantity of the good.
D) will find that consumers are unwilling to purchase the good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions : Scenario: Alexander and Vanessa Alexander and Vanessa benefit from scientific research.Alexander's marginal private benefit from such research is given by the equation MPB = 200 - Q,where Q refers to the amount of research undertaken and MPB captures the marginal private benefit Alexander gets from different marginal quantities.Meanwhile,Vanessa's marginal private benefit from such research is given by the equation MPB = 100 - Q.The marginal social cost of such research is constant at $100. -(Scenario: Alexander and Vanessa) Use Scenario: Alexander and Vanessa.If Alexander and Vanessa are the only two individuals in a society,which equation CORRECTLY represents the marginal social benefit (MSB) of scientific research?
A) MSB = 300 - 2Q
B) MSB = 100 - Q
C) MSB = 200 - Q
D) MSB = 100
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions :
Figure: Market Failure 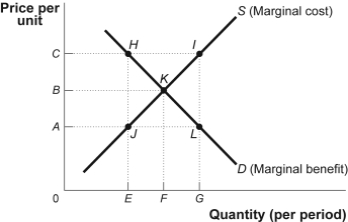 -(Figure: Market Failure) Use Figure: Market Failure.In the figure,if production in this competitive market is at quantity F:
-(Figure: Market Failure) Use Figure: Market Failure.In the figure,if production in this competitive market is at quantity F:
A) marginal benefit is equal to marginal cost.
B) marginal benefit is less than marginal cost.
C) marginal benefit is greater than marginal cost.
D) price is equal to marginal cost and greater than marginal benefit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bluefin tuna travel in schools throughout the world's oceans.Fishing boats from many nations harvest bluefin tuna as the schools migrate through their national waters.The schools of bluefin tuna are BEST described as a(n) :
A) private good.
B) public good.
C) artificially scarce resource.
D) common resource.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the market produces an efficient level of a good,then we know that the good must be _____ and _____ in consumption.
A) nonexcludable;nonrival
B) nonexcludable;rival
C) excludable;nonrival
D) excludable;rival
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which good is MOST likely an artificially scarce good?
A) a ticket to a boxing match
B) pay per view of a boxing match
C) health care
D) the police department
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since the public safety that a police force provides is _____ in consumption,the efficient price _____.
A) rival;is zero
B) nonrival;is zero
C) rival;equals marginal social benefit
D) nonrival;equals marginal social benefit
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions : -(Table: Marginal Benefit,Cost,and Consumer Surplus) Use Table: Marginal Benefit,Cost,and Consumer Surplus.The table shows six consumers' willingness to pay for one iTunes download.If the marginal social cost is constant at _____,then _____ consumers will purchase this good,and consumer surplus is _____.
A) $5.50;two;$14
B) $6;three;$30
C) $6.50;two;$13
D) $3;four;$34
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a common resource,the marginal social benefit at the quantity provided by a private market is _____ the marginal social cost.
A) equal to
B) greater than
C) less than
D) irrelevant to
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Goods that are nonrival in consumption and nonexcludable are _____ goods.
A) common resource
B) private
C) public
D) normal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A software programme is similar to an apple in that it is _____,but it is also similar to public safety in that it is _____.
A) rival in consumption;nonexcludable
B) nonrival in consumption;excludable
C) excludable;nonrival in consumption
D) nonexcludable;rival in consumption
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The BEST example of an artificially scarce good is:
A) legal services.
B) national defence.
C) a municipal library.
D) cable television programming.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A good is MOST likely to be artificially scarce if:
A) it is nonexcludable and nonrival.
B) the seller is a monopolist.
C) it is nonexcludable but rival.
D) it is excludable but nonrival.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In London,any motorist entering a particular area in the city centre during certain specified times must pay a congestion fee equal to £11.50 per day,with fines for noncompliance rising to as high as £130.The congestion fee is:
A) a Pigouvian subsidy aimed at encouraging the use of city streets.
B) an attempt to internalize the costs of traffic delays and congestion.
C) the wrong policy tool for solving the problem of congestion;instead,motorists should be allowed to make deals to determine when and where they are permitted to drive.
D) likely to cause marginal private benefit from road use to decrease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If policy makers provide only enough tradable permits to provide efficient use of a common resource,only those who _____ will use the resource.
A) gain the most
B) initially obtain the permit
C) have the largest market share
D) have monopoly power
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the market does NOT result in an efficient allocation of scarce resources,economists say that there has been:
A) market dropout.
B) normative economics.
C) market disincentives.
D) market failure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Public goods should be produced up to the point at which the marginal cost of production equals:
A) the maximum price any individual is willing to pay for that unit.
B) the sum of the individual marginal benefits from all consumers of that unit.
C) zero,which is the marginal cost of allowing another individual to consume the good.
D) the highest marginal benefit from any individual consumer of the good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Although most citizens have access to police protection,they also take measures,such as putting locks on their doors,to protect themselves.For most citizens,police protection is a(n) _____ good,while self-protection is a(n) _____ good.
A) public;private
B) public;artificially scarce
C) private;private
D) artificially scarce;common resource
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whenever a species is threatened with extinction,it is likely that:
A) clearly defined property rights exist.
B) no one has exclusive property rights to it.
C) greedy people in society are increasing their share of social surplus.
D) it is the result of too much government regulation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a good is subject to the free-rider problem and an inefficiently high level of consumption,the good must be a(n) :
A) private good.
B) public good.
C) common resource.
D) artificially scarce good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 180
Related Exams