A) cycloadditions
B) nucleophilic reactions
C) electrocyclic reactions
D) sigmatropic rearrangements
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the correct classification of the following reaction? 
A) cycloaddition reaction
B) electrophilic reaction
C) electrocyclic reaction
D) sigmatropic reaction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about molecular orbitals is true?
A) The number of molecular orbitals formed is different from the number of atomic orbitals used.
B) The number of molecular orbitals formed is equal to the number of atomic orbitals used.
C) The number of molecular orbitals formed is equal to twice the number of atomic orbitals used.
D) The number of molecular orbitals formed is equal to half the number of atomic orbitals used.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of cycloaddition reaction is shown in the following equation? ![What type of cycloaddition reaction is shown in the following equation? A) [2+2] B) [4+2] C) [4+4] D) [0+2]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5871/11ea9088_7054_a97b_aec7_05475357e065_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00.jpg)
A) [2+2]
B) [4+2]
C) [4+4]
D) [0+2]
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is the Diels-Alder reaction called a thermal [4+2] cycloaddition?
A) Because the reaction is initiated by heat; the diene has four electrons and the dienophile has two electrons.
B) Because the reaction is initiated by light; the diene has four electrons and the dienophile has two electrons.
C) Because the reaction is initiated by heat; the dienophile has four electrons and the diene has two electrons.
D) Because the reaction is initiated by light; the dienophile has four electrons and the diene has two electrons.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about orbitals is true?
A) " orbitals are formed by the linear combination of two sp3 orbitals."
B) " orbitals are formed by the linear combination of two sp2 orbitals."
C) " orbitals are formed by the linear combination of two sp orbitals."
D) " orbitals are formed by the linear combination of two p orbitals."
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about sigmatropic reactions is true?
A) The reactants contain one more bond than the product.
B) The product contains one more bond than the reactant.
C) A bond is broken in the reactant.
D) A bond is broken in the reactant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about sigmatropic reactions is not true?
A) A sigmatropic reaction is an intramolecular pericyclic reaction.
B) In a sigmatropic reaction, bond is broken in one of the reactants.
C) The bonds rearrange in a sigmatropic reaction.
D) The number of bonds in the reactants and product differs in a sigmatropic reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about cycloaddition reactions is true?
A) Cycloaddition reactions can be initiated by heat only.
B) Cycloaddition reactions can be initiated by light only.
C) Cycloaddition reactions can be initiated by heat or light.
D) Cycloaddition reactions are identified by the number of electrons in the two products.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a type of pericyclic reaction?
A) electrocyclic reactions
B) acyclic reactions
C) cycloelimination reactions
D) electrophilic reactions
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the major organic product of the following Claisen rearrangement? 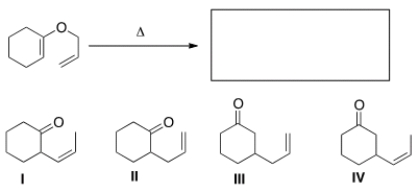
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Predict the major organic product(s) of the following electrocyclic reaction. 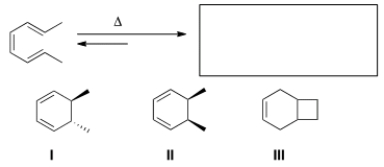
A) Only I
B) Only II
C) Only III
D) Only I and II
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about orbital symmetry and cycloaddition reactions is true?
A) Thermal cycloadditions involving an even number of bonds proceed by a suprafacial pathway.
B) Thermal cycloadditions involving an odd number of bonds proceed by a suprafacial pathway.
C) Photochemical cycloadditions involving an odd number of bonds proceed by a suprafacial pathway.
D) Photochemical sycloadditions involving an even number of bonds proceed by an antarafacial pathway.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of sigmatropic rearrangement is illustrated below? ![What type of sigmatropic rearrangement is illustrated below? A) [1,3] B) [1,4] C) [3,3] D) [1,5]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5871/11ea9088_7055_6ccc_aec7_7b8a2ff856d0_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00_TB5871_00.jpg)
A) [1,3]
B) [1,4]
C) [3,3]
D) [1,5]
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many molecular orbitals are present in 1,3,5-hexatriene?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about orbital symmetry and cycloaddition reactions is true?
A) Thermal cycloadditions involving an even number of bonds proceed by a suprafacial pathway.
B) Thermal cycloaddition involving an odd number of bonds proceed by an antarafacial pathway.
C) Photochemical cycloadditions involving an even number of bonds proceed by an antarafacial pathway.
D) Photochemical cycloadditions involving an even number of bonds proceed by a suprafacial pathway.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about a -bonding molecular orbital is true?
A) A -bonding molecular orbital is formed when two p orbitals of similar phase overlap.
B) A -bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy than a -bonding molecular orbital.
C) A -bonding molecular orbital is formed when two p orbitals of opposite phase overlap.
D) Both the statements "a -bonding molecular orbital is formed when two p orbitals of similar phase overlap" and a -bonding molecular orbital is lower in energy than a -bonding molecular orbital" are true.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the correct classification of the following reaction? 
A) cycloaddition reaction
B) electrocyclic reaction
C) electrophilic reaction
D) sigmatropic reaction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the correct classification of the following reaction? 
A) cycloaddition reaction
B) electrophilic reaction
C) electrocyclic reaction
D) sigmatropic reaction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about thermal electrocyclic reactions is not true?
A) The number of bonds in the conjugated polyene determines whether rotation is conrotatory or disrotatory.
B) Thermal electrocyclic reactions occur in a disrotatory fashion for a conjugated polyene with an odd number of bonds.
C) Thermal electrocyclic reactions occur in a conrotatory fashion for a conjugated polyene with an even number of bonds.
D) In thermal reactions, we consider the orbitals of the HOMO of the ground state electronic configuration to determine the course of the reaction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 52
Related Exams