Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The most common genotype in a population is called the mutant genotype.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A translocation that moves a gene from an area of euchromatin to heterochromatin would typically cause a(n) _______ in the expression of the gene.
A) Reduction
B) Increase
C) Gene expression would remain the same
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
HRR usually uses a sister chromatid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of water is tested for mutagens. The water is subjected to a process known as high pressure liquid chromatography which can separate compounds based on their different biochemical properties. As material leaves the HPLC column its absorbance is measured at UV light which is used to detect a variety of different compounds. These readings were recorded as a trace on a graph (top chart in the figure) . Fractions from the column are collected and then tested in an Ames assay (bottom chart in the figure) . In this assay there were 900 colonies with the solvent alone control. Which fractions contain mutagens? 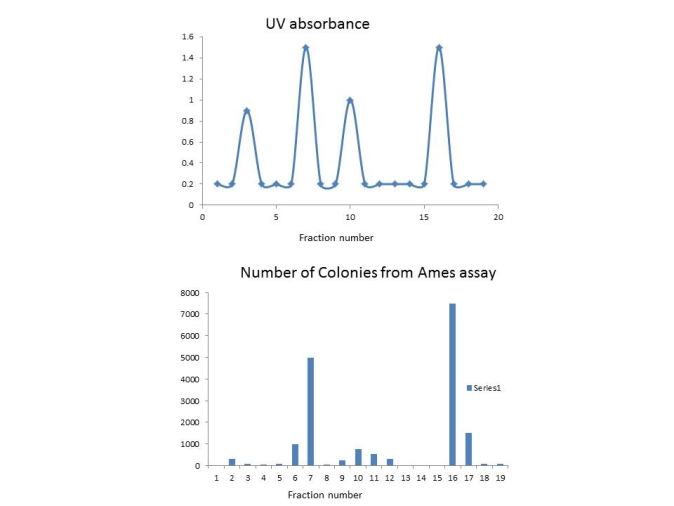
A) 7 and 16
B) 3 and 10
C) 3, 7, 10, and 16
D) None of these fractions appear to contain a mutagen
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
TNRE repeats frequently result in the addition of extra histidine amino acids to the protein.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of a suppressor mutation would be
A) An intragenic mutation that restores the inactive protein's structure
B) An intergenic mutation that increases the activity of a protein performing a different function as the mutated protein
C) An intergenic mutation that activates a transcription factor that increases the espression of a normal protein
D) A mutation that suppresses cell growth
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which types of mutations are least likely to be subjected to natural selection?
A) Silent
B) Missense
C) Nonsense
D) Insertion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Breakpoints in chromosome can lead to mutant phenotypes when they occur in the middle of a gene.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mutations that change the configuration of a protein at a specific temperature are called ____ mutations.
A) Neutral
B) Beneficial
C) Deleterious
D) Conditional
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A heritable change in the genetic material is called a mutation.
Correct Answer

verified
True
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does position effect influence gene expression?
A) Point mutations in promoters frequently occur by this mechanism
B) Translocations may result in a promoter that is normally used for one gene now controlling an entirely different gene.
C) Since this mechanism relies on recombination it relies on the positioning of one allele so that it is under the control of the other allele.
D) Translocations always result in a gene being recombined into an area of heterochromatin.
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An example of a base analog would be
A) EMS
B) Nitrous acid
C) 5BU
D) Nitrogen mustards
E) Acridine dyes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A temporary change in the conformation of a nitrogenous base is called ______.
A) Depurination
B) A tautomeric shift
C) Deamination
D) None of the answers are correct
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A mutation in a promoter region that causes the promoter sequence to more closely resemble the consensus sequence is called an up promoter mutation and results in a decrease in transcription.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A change in the chromosome number is called a point mutation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conversion of cytosine to uracil in DNA is an example of _____.
A) Depurination
B) Tautomeric shifts
C) Deamination
D) Demethylation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which repair mechanism utilizes MutL, MutH, and MutS proteins in
A) Recombinational repair
B) Direct repair
C) Base excision repair
D) Mismatch repair
E) Nucleotide excision repair
F) Nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spontaneous mutations include
A) Depurination, deamination, errors in DNA replication
B) UV light, radiation, deamination, depurination
C) UV light, radiation, deamination, errors in replication
D) UV light, errors in DNA replication, deamination, depurination
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not an example of a induced mutational mechanism?
A) DNA replication errors
B) Tautomeric shifts of nucleic acid bases
C) Aberrant recombination
D) UV light
E) Transposable elements
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 55
Related Exams