A) the enzyme that cuts DNA into restriction fragments.
B) the sticky end of a DNA fragment.
C) a SNP marker.
D) a plasmid used to transfer DNA into a living cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A cell of a particular type, that has the ability to differentiate into other cells of the same tissue type, is a(n) ________ cell.
A) totipotent
B) pluripotent
C) tumour
D) metastatic
E) zygote
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following techniques used to analyze gene function depends on the specificity of DNA base complementarity?
A) gel electrophoresis
B) use of RNAi
C) in vitro mutagenesis
D) in situ hybridization
E) restriction fragment analysis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sequencing an entire genome, such as that of C. elegans, a nematode, is most important because
A) it allows researchers to use the sequence to build a "better" nematode, which is resistant to disease.
B) it allows research on a group of organisms we do not usually care much about.
C) the nematode is a good animal model for trying out cures for viral illness.
D) a sequence that is found to have a particular function in the nematode is likely to have a closely related function in vertebrates.
E) a sequence that is found to have no introns in the nematode genome is likely to have acquired the introns from higher organisms.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
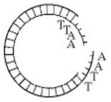 -Which enzyme was used to produce the molecule in the figure above?
-Which enzyme was used to produce the molecule in the figure above?
A) ligase
B) transcriptase
C) a restriction enzyme
D) RNA polymerase
E) DNA polymerase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Genetic engineering is being used by the pharmaceutical industry. Which of the following is not currently one of the uses?
A) production of human insulin
B) production of human growth hormone
C) production of tissue plasminogen activator
D) genetic modification of plants to produce vaccines
E) creation of products that will remove poisons from the human body
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the next few questions. A eukaryotic gene has "sticky ends" produced by the restriction endonuclease EcoRI. The gene is added to a mixture containing EcoRI and a bacterial plasmid that carries two genes conferring resistance to ampicillin and tetracycline. The plasmid has one recognition site for EcoRI located in the tetracycline resistance gene. This mixture is incubated for several hours, exposed to DNA ligase, and then added to bacteria growing in nutrient broth. The bacteria are allowed to grow overnight and are streaked on a plate using a technique that produces isolated colonies that are clones of the original. Samples of these colonies are then grown in four different media: nutrient broth plus ampicillin, nutrient broth plus tetracycline, nutrient broth plus ampicillin and tetracycline, and nutrient broth without antibiotics. -Bacteria that do not take up any plasmids would grow on which media?
A) the nutrient broth only
B) the nutrient broth and the tetracycline broth
C) the nutrient broth and the ampicillin broth
D) the tetracycline broth and the ampicillin broth
E) all three broths
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is (are) about restriction enzymes? I. They are used by bacteria to cut up foreign DNA. II. They cut DNA unevenly to produce "sticky ends." III. They are non-specific and cut anywhere along a sequence. IV. They are involved with heterochromatin production.
A) I only
B) IV only
C) I and II
D) I, II, and III
E) III and IV
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A principal problem with inserting an unmodified mammalian gene into a plasmid, and then getting that gene expressed in bacteria, is that
A) prokaryotes use a different genetic code from that of eukaryotes.
B) bacteria translate polycistronic messages only.
C) bacteria cannot remove eukaryotic introns.
D) bacterial RNA polymerase cannot make RNA complementary to mammalian DNA.
E) bacterial DNA is not found in a membrane-bounded nucleus and is therefore incompatible with mammalian DNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To introduce a particular piece of DNA into an animal cell, such as that of a mouse, you would find more probable success with which of the following methods?
A) the shotgun approach
B) electroporation followed by recombination
C) introducing a plasmid into the cell
D) infecting the mouse cell with a Ti plasmid
E) transcription and translation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the next few questions. CML (chronic myelogenous leukemia) results from a translocation between human chromosomes 9 and 22. The resulting chromosome 22 is significantly shorter than usual, and it is known as a Philadelphia (Ph') chromosome. The junction at the site of the translocation causes overexpression of a thymine kinase receptor. A new drug (Gleevec or imatinib) has been found to inhibit the disease if the patient is treated early. -One possible use of transgenic plants is in the production of human proteins, such as vaccines. Which of the following is a possible hindrance that must be overcome?
A) prevention of transmission of plant allergens to the vaccine recipients
B) prevention of vaccine-containing plants being consumed by insects
C) use of plant cells to translate non-plant-derived mRNA
D) inability of the human digestive system to accept plant-derived protein
E) the need to cook all such plants before consuming them
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA technology has many medical applications. Which of the following is not done routinely at present?
A) production of hormones for treating diabetes and dwarfism
B) production of microbes that can metabolize toxins
C) introduction of genetically engineered genes into human gametes
D) prenatal identification of genetic disease alleles
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Genetically engineered plants
A) are more difficult to engineer than animals.
B) include a transgenic rice plant that can help prevent vitamin A deficiency.
C) are being rapidly developed, but traditional plant breeding programs are still the only method used to develop new plants.
D) are able to fix nitrogen themselves.
E) are banned throughout the world.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below. The DNA profiles that follow represent four different individuals.
 -Which of the following are probably siblings?
-Which of the following are probably siblings?
A) A and B
B) A and C
C) A and D
D) C and D
E) B and D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. Spider silk is one of the strongest biomolecules known. It has a tensile strength greater than Kevlar and elasticity greater than rubber. Attempts to "farm" spiders have met with little success (they tend to eat each other) . Researchers have identified the gene responsible for the formation of the silk. -Researchers have successfully inserted this gene into goats. These "spidergoats" live a normal life. The silk protein is expressed and extracted from their milk. This is quite controversial; why not manufacture the silk from E.coli?
A) E.coli cannot be transformed.
B) Spiders are eukaryotic and their genes must be inserted into another eukaryote.
C) The silk protein would be mixed with other protein products in E.coli.
D) The sheer volume of protein extracted from milk makes it more economical.
E) Goats are more closely related to spiders than bacteria.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA microarrays have made a huge impact on genomic studies because they
A) can be used to eliminate the function of any gene in the genome.
B) can be used to introduce entire genomes into bacterial cells.
C) allow the expression of many or even all of the genes in the genome to be compared at once.
D) allow physical maps of the genome to be assembled in a very short time.
E) dramatically enhance the efficiency of restriction enzymes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does a bacterial cell protect its own DNA from restriction enzymes?
A) by adding methyl groups to adenines and cytosines
B) by using DNA ligase to seal the bacterial DNA into a closed circle
C) by adding histones to protect the double-stranded DNA
D) by forming "sticky ends" of bacterial DNA to prevent the enzyme from attaching
E) by reinforcing the bacterial DNA structure with covalent phosphodiester bonds
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One successful form of gene therapy has involved delivery of an allele for the enzyme adenosine deaminase (ADA) to bone marrow cells of a child with SCID, and delivery of these engineered cells back to the bone marrow of the affected child. What is one major reason for the success of this procedure as opposed to many other efforts at gene therapy?
A) The engineered bone marrow cells from this patient can be used for any other SCID patient.
B) The ADA-introduced allele causes all other ADA-negative cells to die.
C) The engineered cells, when reintroduced into the patient, find their way back to the bone marrow.
D) No vector is required to introduce the allele into ADA-negative cells.
E) The immune system fails to recognize cells with the variant gene.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would not be true of cDNA produced using human brain tissue as the starting material?
A) It could be amplified by the polymerase chain reaction.
B) It was produced from pre-mRNA using reverse transcriptase.
C) It could be labelled and used as a probe to detect genes expressed in the brain.
D) It lacks the introns of the pre-MRNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The first cloned cat, called Carbon Copy, was a calico, but she looked significantly different from her female parent. Why?
A) The environment, as well as genetics, affects phenotypic variation.
B) Fur-colour genes in cats are influenced by differential acetylation patterns.
C) Cloned animals have been found to have a higher frequency of transposon activation.
D) X inactivation in the embryo is random and produces different patterns.
E) The telomeres of the parent's chromosomes were shorter than those of an embryo.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 72
Related Exams