A) Mutant mice were resistant to bacterial infections.
B) Mixing a heat-killed pathogenic strain of bacteria with a living nonpathogenic strain can convert some of the living cells into the pathogenic form.
C) Mixing a heat-killed nonpathogenic strain of bacteria with a living pathogenic strain makes the pathogenic strain nonpathogenic.
D) Infecting mice with nonpathogenic strains of bacteria makes them resistant to pathogenic strains.
E) Mice infected with a pathogenic strain of bacteria can spread the infection to other mice.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is meant by the description "antiparallel" regarding the strands that make up DNA?
A) The twisting nature of DNA creates nonparallel strands.
B) The 5' to 3' direction of one strand runs counter to the 5' to 3' direction of the other strand.
C) Base pairings create unequal spacing between the two DNA strands.
D) One strand is positively charged and the other is negatively charged.
E) One strand contains only purines and the other contains only pyrimidines.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To repair a thymine dimer by nucleotide excision repair, in which order do the necessary enzymes act?
A) exonuclease, DNA polymerase III, RNA primase
B) helicase, DNA polymerase I, DNA ligase
C) DNA ligase, nuclease, helicase
D) DNA polymerase I, DNA polymerase III, DNA ligase
E) endonuclease, DNA polymerase I, DNA ligase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following investigator(s) was/were responsible for the following discovery? In DNA from any species, the amount of adenine equals the amount of thymine, and the amount of guanine equals the amount of cytosine.
A) Frederick Griffith
B) Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
C) Oswald Avery, Maclyn McCarty, and Colin MacLeod
D) Erwin Chargaff
E) Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents the order of increasingly higher levels of organization of chromatin?
A) nucleosome, 30-nm chromatin fibre, looped domain
B) looped domain, 30-nm chromatin fibre, nucleosome
C) looped domain, nucleosome, 30-nm chromatin fibre
D) nucleosome, looped domain, 30-nm chromatin fibre
E) 30-nm chromatin fibre, nucleosome, looped domain
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you are provided with an actively dividing culture of E. coli bacteria to which radioactive thymine has been added. What would happen if a cell replicates once in the presence of this radioactive base?
A) One of the daughter cells, but not the other, would have radioactive DNA.
B) Neither of the two daughter cells would be radioactive.
C) All four bases of the DNA would be radioactive.
D) Radioactive thymine would pair with nonradioactive guanine.
E) DNA in both daughter cells would be radioactive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
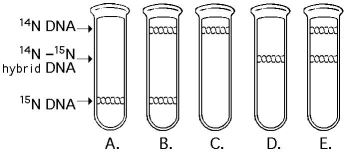 -In the late 1950s, Meselson and Stahl grew bacteria in a medium containing "heavy" nitrogen (¹⁵N) and then transferred them to a medium containing ¹⁴N. Which of the results in the figure above would be expected after one round of DNA replication in the presence of ¹⁴N?
-In the late 1950s, Meselson and Stahl grew bacteria in a medium containing "heavy" nitrogen (¹⁵N) and then transferred them to a medium containing ¹⁴N. Which of the results in the figure above would be expected after one round of DNA replication in the presence of ¹⁴N?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In trying to determine whether DNA or protein is the genetic material, Hershey and Chase made use of which of the following facts?
A) DNA contains sulPHur, whereas protein does not.
B) DNA contains phosphorus, whereas protein does not.
C) DNA contains nitrogen, whereas protein does not.
D) DNA contains purines, whereas protein includes pyrimidines.
E) RNA includes ribose, whereas DNA includes deoxyribose sugars.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In analyzing the number of different bases in a DNA sample, which result would be consistent with the base-pairing rules?
A) A = G
B) A + G = C + T
C) A + T = G + T
D) A = C
E) G = T
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You briefly expose bacteria undergoing DNA replication to radioactively labelled nucleotides. When you centrifuge the DNA isolated from the bacteria, the DNA separates into two classes. One class of labelled DNA includes very large molecules (thousands or even millions of nucleotides long) , and the other includes short stretches of DNA (several hundred to a few thousand nucleotides in length) . These two classes of DNA probably represent
A) leading strands and Okazaki fragments.
B) lagging strands and Okazaki fragments.
C) Okazaki fragments and RNA primers.
D) leading strands and RNA primers.
E) RNA primers and mitochondrial DNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The enzyme telomerase solves the problem of replication at the ends of linear chromosomes by which method?
A) adding a single 5' cap structure that resists degradation by nucleases
B) causing specific double-strand DNA breaks that result in blunt ends on both strands
C) causing linear ends of the newly replicated DNA to circularize
D) adding numerous short DNA sequences such as TTAGGG
E) adding numerous GC pairs that resist hydrolysis and maintain chromosome integrity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
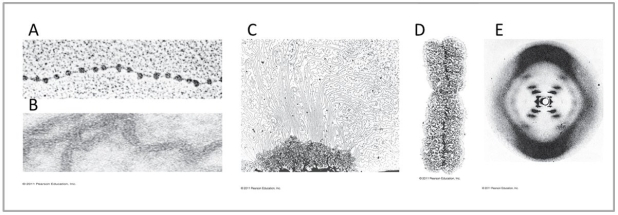 The images above are of DNA at various levels of coiling and folding. Use this image to answer the questions below.
-Which image shows scaffolding?
The images above are of DNA at various levels of coiling and folding. Use this image to answer the questions below.
-Which image shows scaffolding?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The hydrolysis of the pyrophosphate in DNA replication is
A) endergonic.
B) exergonic.
C) isotonic.
D) exothermic.
E) a mutation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following help(s) to hold the DNA strands apart while they are being replicated?
A) primase
B) ligase
C) DNA polymerase
D) single-strand binding proteins
E) exonuclease
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After mixing a heat-killed, phosphorescent strain of bacteria with a living nonphosphorescent strain, you discover that some of the living cells are now phosphorescent. Which observations would provide the best evidence that the ability to fluoresce is a heritable trait?
A) DNA passed from the heat-killed strain to the living strain.
B) Protein passed from the heat-killed strain to the living strain.
C) The phosphorescence in the living strain is especially bright.
D) Descendants of the living cells are also phosphorescent.
E) Both DNA and protein passed from the heat-killed strain to the living strain.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
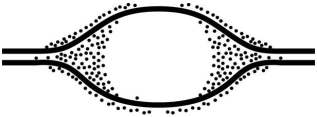 Grains represent radioactive material within the replicating eye.
-In an experiment, DNA is allowed to replicate in an environment with all necessary enzymes, dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and radioactively labeled dTTP (³H thymidine) for several minutes and then switched to nonradioactive medium. It is then viewed by electron microscopy and autoradiography. The figure above represents the results. Which of the following is the most likely interpretation?
Grains represent radioactive material within the replicating eye.
-In an experiment, DNA is allowed to replicate in an environment with all necessary enzymes, dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and radioactively labeled dTTP (³H thymidine) for several minutes and then switched to nonradioactive medium. It is then viewed by electron microscopy and autoradiography. The figure above represents the results. Which of the following is the most likely interpretation?
A) There are two replication forks going in opposite directions.
B) Thymidine is only being added where the DNA strands are furthest apart.
C) Thymidine is only added at the very beginning of replication.
D) Replication proceeds in one direction only.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a nucleosome, the DNA is wrapped around
A) polymerase molecules.
B) ribosomes.
C) histones.
D) a thymine dimer.
E) satellite DNA.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One major difference in prokaryote replication versus eukaryote replication is
A) prokaryotic chromosomes have histones, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes do not.
B) prokaryotic chromosomes have a single origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes have many.
C) the rate of elongation during DNA replication is slower in prokaryotes than in eukaryotes.
D) prokaryotes produce Okazaki fragments during DNA replication, but eukaryotes do not.
E) prokaryotes have telomeres, and eukaryotes do not.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An Okazaki fragment has which of the following arrangements?
A) primase, polymerase, ligase
B) 3' RNA nucleotides, DNA nucleotides 5'
C) 5' RNA nucleotides, DNA nucleotides 3'
D) DNA polymerase I, DNA polymerase III
E) 5' DNA to 3'
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes chromatin?
A) Heterochromatin is composed of DNA, whereas euchromatin is made of DNA and RNA.
B) Both heterochromatin and euchromatin are found in the cytoplasm.
C) Heterochromatin is highly condensed, whereas euchromatin is less compact.
D) Euchromatin is not transcribed, whereas heterochromatin is transcribed.
E) Only euchromatin is visible under the light microscope.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 67
Related Exams