A) producing primarily proteins for secretion.
B) producing primarily cytoplasmic proteins.
C) constructing an extensive cell wall or extracellular matrix.
D) digesting large food particles.
E) enlarging its vacuole.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The smallest cell structure that would most likely be visible with a standard (not super-resolution) research-grade light microscope is
A) a mitochondrion.
B) a microtubule.
C) a ribosome.
D) a microfilament.
E) a nuclear pore.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mutation that disrupts the ability of an animal cell to add polysaccharide modifications to proteins would most likely cause defects in its
A) nuclear lamina and nuclear matrix.
B) nuclear matrix and extracellular matrix.
C) mitochondria and Golgi apparatus.
D) Golgi apparatus and extracellular matrix.
E) nuclear pores and secretory vesicles.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which organelle is the primary site of ATP synthesis in eukaryotic cells?
A) lysosome
B) vacuole
C) mitochondrion
D) Golgi apparatus
E) peroxisome
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nuclear lamina is an array of filaments on the inner side of the nuclear membrane. If a method were found that could cause the lamina to fall into disarray, what would you expect to be the most likely consequence?
A) the loss of all nuclear function
B) the inability of the nucleus to divide during cell division
C) a change in the shape of the nucleus
D) failure of chromosomes to carry genetic information
E) inability of the nucleus to keep out destructive chemicals
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the trees in this figure groups the domains according to similarities in cellular size and architecture? 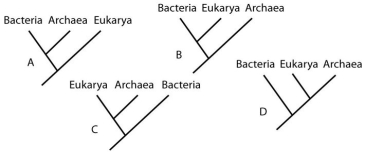
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The volume enclosed by the plasma membrane of plant cells is often much larger than the corresponding volume in animal cells. The most reasonable explanation for this observation is that
A) plant cells are capable of having a much higher surface-to-volume ratio than animal cells.
B) plant cells have a much more highly convoluted (folded) plasma membrane than animal cells.
C) plant cells contain a large vacuole that reduces the volume of the cytoplasm.
D) animal cells are more spherical, whereas plant cells are elongated.
E) plant cells can have lower surface-to-volume ratios than animal cells because plant cells synthesize their own nutrients.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
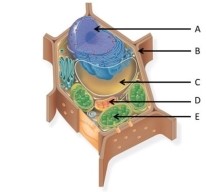 -Which two structures are shared by all eukaryotic cells?
-Which two structures are shared by all eukaryotic cells?
A) A and C
B) A and D
C) B and D
D) B and E
E) C and E
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the fractionation of homogenized cells using centrifugation, the primary factor that determines whether a specific cellular component ends up in the supernatant or the pellet is
A) the relative solubility of the component.
B) the size and weight of the component.
C) the percentage of carbohydrates in the component.
D) the presence or absence of nucleic acids in the component.
E) the presence or absence of lipids in the component.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which structure is the site of the synthesis of proteins that may be exported from the cell?
A) rough ER
B) lysosomes
C) plasmodesmata
D) Golgi vesicles
E) free cytoplasmic ribosomes
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Recent evidence shows that when chromosomes decondense during interphase, their DNA molecules do not intermingle. Instead, they occupy distinct territories within the nucleus. Considering the structure and location of the following structures, which is most likely to be involved in chromosome location?
A) nuclear pores
B) the nucleolus
C) microfilaments
D) the nuclear lamina and matrix
E) the nuclear envelope
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A primary objective of cell fractionation is to
A) view the structure of cell membranes.
B) sort cells based on their size and weight.
C) determine the size of various organelles.
D) separate the major organelles so that their particular functions can be determined.
E) separate lipid-soluble from water-soluble molecules.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cells require which of the following to form cilia or flagella?
A) centrosomes
B) laminin
C) actin
D) intermediate filaments
E) secretory vesicles
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
ECM proteins are made by ribosomes in which part of a eukaryotic cell?
A) mitochondria
B) cytoplasm
C) nuclear envelope
D) Golgi apparatus
E) rough ER
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fact that the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope has bound ribosomes allows one to most reliably conclude that
A) at least some of the proteins that function in the nuclear envelope are made by the ribosomes on the nuclear envelope.
B) the nuclear envelope is not part of the endomembrane system.
C) the nuclear envelope is physically separated from the endoplasmic reticulum.
D) small vesicles from the Golgi fuse with the nuclear envelope.
E) nuclear pore complexes contain proteins.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the cytoskeleton is true?
A) The dynamic aspect of cytoskeletal function is made possible by the assembly and disassembly of a large variety of proteins into complex aggregates.
B) Microfilaments are structurally rigid and resist compression, whereas microtubules resist tension (stretching) .
C) Movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other.
D) Chemicals that block the assembly of the cytoskeleton would cause little effect on the cell's response to external signals and stimuli.
E) Transport vesicles among the membranes of the endomembrane system produce the cytoskeleton.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following contains hydrolytic enzymes?
A) lysosome
B) vacuole
C) mitochondrion
D) Golgi apparatus
E) peroxisome
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
 -What is the function of the structure labelled E?
-What is the function of the structure labelled E?
A) respiration
B) photosynthesis
C) maintain cell pressure
D) contain DNA
E) synthesize lipids
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ions can travel directly from the cytoplasm of one animal cell to the cytoplasm of an adjacent cell through
A) plasmodesmata.
B) intermediate filaments.
C) tight junctions.
D) desmosomes.
E) gap junctions.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below. You are investigating different live cells using a light microscope. The first cells you observe are part of a larger organism. They have a clear area in the middle, a defined shape, and you can see many greenish ovals pressed up along the outer edges. -The movement inside the cells that you observed are a result of
A) cilia movement.
B) the interaction of actin and myosin filaments.
C) the extracellular matrix.
D) cell division.
E) intermediate filaments.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 96
Related Exams