A) produce movement
B) maintain posture
C) maintain body temperature
D) guard body entrances and exits
E) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an isotonic contraction,
A) muscle tension exceeds the load and the muscle lifts the load.
B) tension rises and falls but the muscle length is constant.
C) the peak tension is less than the load.
D) many twitches fuse into one.
E) flexion is produced.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
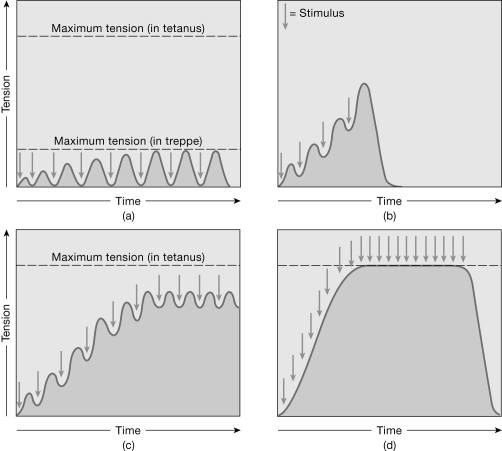 Figure 9-2 Muscle Contractions
Use Figure 9-2 to answer the following questions:
-What is the contraction in graph (d) called?
Figure 9-2 Muscle Contractions
Use Figure 9-2 to answer the following questions:
-What is the contraction in graph (d) called?
A) complete tetanus
B) incomplete tetanus
C) twitch
D) wave summation
E) treppe
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How would a drug that blocks acetylcholine receptors at the motor end plate affect skeletal muscle?
A) It would make the muscles more excitable.
B) It would produce uncontrolled muscle spasms.
C) It would cause spastic paralysis (muscles are contracted and unable to relax) .
D) It would cause flaccid paralysis (muscles are relaxed and unable to contract) .
E) It would have little effect on skeletal muscles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nerves and blood vessels that service the muscle fibers are located in the connective tissues of the
A) endomysium.
B) perimysium.
C) sarcolemma.
D) sarcomere.
E) myofibrils.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The types of muscle tissue include all of the following, except
A) striated muscle.
B) cardiac muscle.
C) smooth muscle.
D) skeletal muscle.
E) none of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Heat energy produced from muscle contraction is released by the ________ system.
A) integumentary
B) respiratory
C) cardiovascular
D) urinary
E) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the term titin?
A) protein that accounts for elasticity of resting muscle
B) repeating unit of striated myofibrils
C) storage site for calcium ions
D) where thin filaments are anchored
E) largely made of myosin molecules
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Muscle tissue, one of the four basic tissue groups, consists chiefly of cells that are highly specialized for
A) conduction.
B) contraction.
C) peristalsis.
D) cushioning
E) any of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Individual muscle cells are surrounded by
A) endomysium.
B) perimysium.
C) sarcolemma.
D) sarcomere.
E) myofibrils.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When comparing slow motor units to fast motor units, slow units
A) take about three times as long to reach peak tension.
B) have much smaller fiber diameters.
C) generate much less tension.
D) are rich in the red protein myoglobin.
E) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rapid rise and fall in force produced by a muscle fiber after a single action potential is
A) a tetanus.
B) an unfused tetanus.
C) a twitch.
D) an end plate potential.
E) a muscle action potential.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Physical evidence that supports the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction includes
A) constant distance between Z lines during contraction.
B) decreased width of the H band during contraction.
C) increased width of the I band during contraction.
D) decreased width of the A band during contraction.
E) the I band and H band distance is constant during contraction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these would lead to increased oxygen consumption?
A) increased heat production
B) increased conversion of lactic acid to glucose
C) increased aerobic respiration by muscle cells
D) increased muscle activity
E) all of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In response to action potentials arriving along the transverse tubules, the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases
A) acetylcholine.
B) sodium ions.
C) potassium ions.
D) calcium ions.
E) hydrogen ions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 115 of 115
Related Exams