A) transitional cells.
B) circular folds.
C) elastic cells.
D) rugae.
E) muscularis mucosa.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true regarding the production of intestinal juice?
A) Most of the fluid is actively transported into the lumen.
B) The pancreas is the source for most of the intestinal juice.
C) Intestinal juice is produced following activation by motilin.
D) Local reflexes and parasympathetic stimulation increase the production of intestinal juice.
E) The cephalic phase of gastric secretion produces intestinal juice.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A drug that blocks the action of the hormone cholecystokinin would affect all of the following except
A) relaxation of the hepatopancreatic sphincter.
B) the composition of pancreatic secretions.
C) the delivery of bile.
D) digestion of lipids and proteins.
E) absorption of water in the large intestines.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Functions of the tongue include all of the following except
A) mechanical processing of food.
B) manipulation of food.
C) sensory analysis of food.
D) aiding in speech.
E) partitioning the oropharynx from the nasopharynx.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stimulation of gastric stretch receptors causes all of the following except
A) a decrease in myenteric plexus stimulation.
B) an increase in histamine release.
C) an increase in gastrin secretion.
D) an increase in submucosal neural plexus stimulation.
E) an increase in acid production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not found in the large intestines?
A) villi
B) intestinal crypts
C) intestinal glands
D) mucous cells
E) simple columnar epithelium
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The part of a tooth that contains blood vessels and nerves is the
A) enamel.
B) cement.
C) dentin.
D) pulp cavity.
E) periodontium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In response to the hormone cholecystokinin, the pancreas secretes a fluid
A) rich in enzymes.
B) rich in bicarbonate.
C) rich in bile.
D) rich in mucus.
E) that contains only amylase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chief cells secrete
A) pepsinogen.
B) gastrin.
C) mucus.
D) hydrochloric acid.
E) intrinsic factor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During deglutition, which of the following phases is first?
A) buccal
B) pharyngeal
C) gastric
D) esophageal
E) enteric
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An intestinal hormone that stimulates mucin production by the submucosal duodenal glands is
A) secretin.
B) cholecystokinin.
C) enterocrinin.
D) GIP.
E) gastrin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a reason the stomach is acidic?
A) Kills microorganisms.
B) Emulsification of lipids.
C) Denatures proteins.
D) Helps break down plant cell walls and connective tissue in meat.
E) Activates pepsin.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The root of a tooth is covered by
A) enamel.
B) cement.
C) dentin.
D) pulp.
E) the root canal.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Triglycerides, steroids, phospholipids and fat-soluble vitamins that are coated with proteins are called
A) lacteals.
B) chylomicrons.
C) vesicles.
D) micelles.
E) bile salts.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Circular folds and intestinal villi
A) increase the surface area of the mucosa of the small intestine.
B) carry products of digestion that will not pass through the walls of blood capillaries.
C) produce new cells for the mucosa of the small intestine.
D) secrete digestive enzymes.
E) produce hormones.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hydrochloric acid from the stomach is neutralized in the small intestine by
A) water that was ingested with the food.
B) bicarbonate from the pancreas.
C) trypsin.
D) bile from the liver.
E) enzymes from the intestinal crypts.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 24-2 The Wall of the Small Intestine
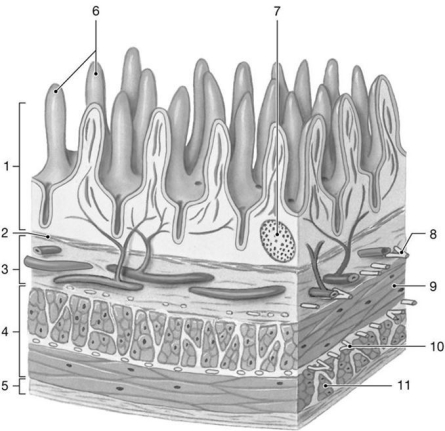 Use Figure 24-2 to answer the following questions:
-What type of epithelium covers the structure labeled "6"?
Use Figure 24-2 to answer the following questions:
-What type of epithelium covers the structure labeled "6"?
A) simple squamous
B) stratified squamous
C) simple cuboidal
D) simple columnar
E) pseudostratified ciliated columnar
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a digestive enzyme?
A) amylase
B) lipase
C) bile
D) pepsin
E) trypsin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
D cells release ________, which inhibits the release of gastrin.
A) inhibin
B) ghrelin
C) leptin
D) somatostatin
E) pepsin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Powerful peristaltic contractions that occur a few times each day in the colon are called
A) segmentation.
B) pendular movements.
C) haustral churning.
D) defecation.
E) mass movements.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 213
Related Exams