A) subsidize production by $20 per unit.
B) subsidize production by $10 per unit.
C) provide the good itself.
D) tax production by $10 per unit.
E) tax production by $20 per unit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three ways governments can encourage production of goods with external benefits are
A) private subsidies, pollution permits, and intellectual property rights.
B) private subsidies, pollution permits, and vouchers.
C) intellectual property rights, pollution permits, and vouchers.
D) taxes, emission charges, and pollution permits.
E) private subsidies, vouchers, and intellectual property rights.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following illustrates the concept of external cost?
A) Bad weather reduces the size of the wheat crop.
B) A reduction in the size of the wheat crop causes income of wheat farmers to fall.
C) Smoking harms the health of the smoker.
D) Smoking harms the health of nearby nonsmokers.
E) Public health services reduce the transmission of disease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
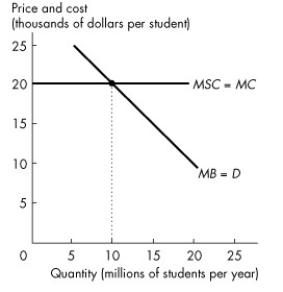 Figure 16.3.3
-Refer to Figure 16.3.3.The figure shows the marginal private benefit and marginal social cost of a university education.Society's external benefit from university graduates is $10,000 each.With no subsidy,
Figure 16.3.3
-Refer to Figure 16.3.3.The figure shows the marginal private benefit and marginal social cost of a university education.Society's external benefit from university graduates is $10,000 each.With no subsidy,
A) no students go to university.
B) less than 10 million students go to university.
C) 10 million students go to university.
D) more than 10 million students go to university.
E) the market is efficient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 16.2.2
Chemical Fertilizer Market
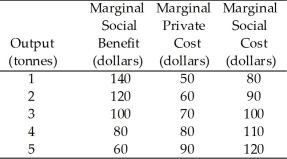 -Refer to Table 16.2.2.The Pigovian tax that achieves the efficient quantity of output is
-Refer to Table 16.2.2.The Pigovian tax that achieves the efficient quantity of output is
A) $0.
B) $10 a tonne.
C) $20 a tonne.
D) $30 a tonne.
E) $40 a tonne.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
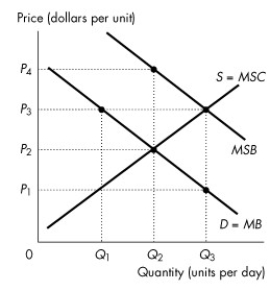 Figure 16.3.1
-Refer to Figure 16.3.1.The figure shows the marginal private benefit curve, the marginal social benefit curve, and the market supply curve.If a subsidy is granted that generates an efficient quantity, then the quantity produced is
Figure 16.3.1
-Refer to Figure 16.3.1.The figure shows the marginal private benefit curve, the marginal social benefit curve, and the market supply curve.If a subsidy is granted that generates an efficient quantity, then the quantity produced is
A) zero.
B) Q₁.
C) Q₂.
D) Q₃.
E) greater than Q₃.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the production of a good has an external cost, the
A) marginal social cost curve lies below the marginal private cost curve.
B) marginal social benefit curve lies above the marginal private benefit curve.
C) equilibrium quantity in an unregulated, competitive market has a marginal social cost greater than the marginal social benefit.
D) equilibrium quantity in an unregulated, competitive market has a marginal social cost less than the marginal social benefit.
E) good should not be produced.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If negative externalities exist, then in a market with no property rights,
A) MSC = MSB.
B) MSC < MSB.
C) MSC > MSB.
D) MSC = marginal external cost.
E) MC > MSC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which one of the following is a means of coping with a negative externality?
A) emission subsidies
B) patents
C) vouchers
D) Pigovian taxes
E) copyrights
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A system of cap-and-trade is used to reduce acid rain caused by emissions from electric power utilities.Which of the following statements is true?
A) Market forces determine both the demand for pollution permits and their supply.
B) Public choice determines both the demand for pollution permits and their supply.
C) Market forces determine the demand for pollution permits, and property rights determine their supply.
D) Property rights determine the demand for pollution permits, and the government determines their supply.
E) Market forces determine the demand for marketable permits, and the government determines their supply.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A battery acid producer pollutes the water upstream from the Polar Bear Club, a swimming club.If transactions costs are low, the quantity of pollution will be efficient
A) only if Ronald Coase is a member of the Polar Bear Club.
B) only if Ronald Coase is not a member of the Polar Bear Club.
C) only if water property rights are assigned to the producer.
D) only if water property rights are assigned to the Polar Bear Club.
E) if water property rights are assigned either to the producer or to the Polar Bear Club.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A private cost of production is a cost that is borne by the ________ of a good or service. A social cost of production is a cost that is ________.
A) consumer; borne by the producer and by everyone else on whom the cost falls
B) consumer; not borne by the producer but borne by other people
C) producer; not borne by the producer but borne by other people
D) producer; borne by the producer and by everyone else on whom the cost falls
E) producer; borne by the consumer
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The outcome from a voucher scheme is efficient when the government makes the value of the voucher equal to
A) marginal external cost.
B) marginal external benefit.
C) private external cost.
D) private external benefit.
E) marginal social cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patent is an example of
A) a subsidy.
B) a pollution permit.
C) a voucher.
D) a tax.
E) a legal device for creating property rights.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Environment Canada was created in
A) 1971.
B) 1961.
C) 1981.
D) 1991.
E) 2001.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A private subsidy on a good
A) is similar to a tax because it decreases the production of the good being subsidized.
B) increases demand for the good.
C) punishes those who consume or produce the subsidized good.
D) has no effect on the quantity of the good produced.
E) increases production of that good.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
CoolU has solved its smoking problem by allocating each student 5 smoking permits a day, and allowing trading.This is an example of
A) cap-and-trade.
B) emission charges.
C) the Coase theorem.
D) a pollution tax.
E) a voucher.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider some type of industrial pollution that generates air pollution.This industry, if left unregulated, will produce
A) more than the efficient level because they will ignore the marginal external costs.
B) the efficient level of output.
C) less than the efficient level because they will ignore the marginal external costs.
D) less than the efficient level because they will ignore the marginal external benefits.
E) more than the efficient level because they will ignore the marginal external benefits.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An externality is
A) the amount by which price exceeds marginal private cost.
B) the amount by which price exceeds marginal social cost.
C) the effect of government regulation on market price and output.
D) someone who consumes a good without paying for it.
E) a cost or benefit that arises from an activity but affects people not part of the original activity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure below to answer the following questions.
 Figure 16.3.1
-Refer to Figure 16.3.1.The figure shows the marginal private benefit curve, the marginal social benefit curve, and the market supply curve.If production is left to the private market, then the price is
Figure 16.3.1
-Refer to Figure 16.3.1.The figure shows the marginal private benefit curve, the marginal social benefit curve, and the market supply curve.If production is left to the private market, then the price is
A) P₁.
B) P₃.
C) P₂.
D) greater than P₄.
E) P₄.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 116
Related Exams