A) and market bystanders are both directly affected.
B) and market bystanders are both indirectly affected.
C) is directly affected, and market bystanders are indirectly affected.
D) is indirectly affected, and market bystanders are directly affected.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A local laundry advertises that the clothes it washes smell "sunshine fresh" because it line dries everything outside.Then a steel factory moves in next door and emits black smoke which stains the clothes drying at the laundry.According to the Coase theorem,granting the
A) steel factory the right to pollute would be efficient, but granting the laundry the right to clean air would be equitable.
B) laundry the right to clean air would be efficient, but granting the steel factory the right to pollute would be equitable.
C) steel factory the right to pollute has the same effect on equity as granting the laundry the right to clean air.
D) steel factory the right to pollute has the same effect on efficiency as granting the laundry the right to clean air.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-4
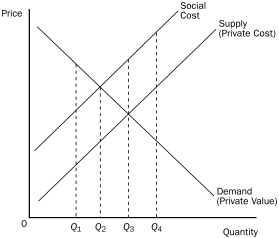 -Refer to Figure 10-4.At Q₃
-Refer to Figure 10-4.At Q₃
A) the marginal consumer values this product less than the social cost of producing it.
B) every consumer values this product less than the social cost of producing it.
C) the cost to society is equal to the value to society.
D) the marginal consumer values this product more than the private cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Anita enjoys growing flowers in her yard and has a lot of spare time,but she can't afford the $100 it costs to buy flower seeds,fertilizer and water.Sally,who has a good view of Anita's yard,would also enjoy Anita's flowers.Sally has plenty of money but has no time to plant flowers.According to the Coase theorem,
A) the city government should give Anita the $100 needed to grow flowers.
B) the city government should require Anita to grow flowers.
C) Sally and Anita could both be better off if Sally gave $100 to Anita to plant flowers.
D) Sally and Anita would both be better off if Sally gave $100 to Anita to plant flowers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between social cost and private cost is a measure of the
A) loss in profit to the seller as the result of a negative externality.
B) cost of an externality.
C) cost reduction when the negative externality is eliminated.
D) cost incurred by the government when it intervenes in the market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term market failure refers to
A) a market that fails to allocate resources efficiently.
B) an unsuccessful advertising campaign which reduces demand.
C) ruthless competition among firms.
D) a firm that is forced out of business because of losses.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a market economy,government intervention
A) will always improve market outcomes.
B) reduces efficiency in the presence of externalities.
C) may improve market outcomes in the presence of externalities.
D) is necessary to control individual greed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that flu shots create a positive externality equal to $12 per shot.Further suppose that the government offers a $15 per-shot subsidy to producers.What is the relationship between the equilibrium quantity and the socially optimal quantity of flu shots produced?
A) They are equal.
B) The equilibrium quantity is greater than the socially optimal quantity.
C) The equilibrium quantity is less than the socially optimal quantity.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What economic argument suggests that if transactions costs are sufficiently low,the equilibrium is economically efficient regardless of how property rights are distributed?
A) the Coase theorem
B) the laws of supply and demand
C) the law of comparative advantage
D) the law of externalities
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Private markets fail to reach a socially optimal equilibrium when positive externalities are present because the
A) private benefit equals the social benefit at the private market solution.
B) private cost exceeds the private benefit at the private market solution.
C) social value exceeds the private value at the private market solution.
D) private cost exceeds the social benefit at the private market solution.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that a negative externality is created by the production of good X.Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The social cost of producing good X includes the private cost plus the cost to bystanders of the externality.
B) The increased social cost can be graphed as a decrease in demand.
C) The market equilibrium quantity will be the socially optimal quantity as long as the government does not interfere.
D) Both a and b are correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a characteristic of pollution permits?
A) Prices are set by supply and demand.
B) Allowing firms to trade their permits reduces the total quantity of pollution beyond the initial allocation.
C) Real-world markets for pollution permits include sulfur dioxide and carbon.
D) Firms for whom pollution reduction is very expensive are willing to pay more for permits than firms for whom pollution reduction is less expensive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-4
 -Refer to Figure 10-4.Externalities in this market could be internalized if
-Refer to Figure 10-4.Externalities in this market could be internalized if
A) there were a tax on the product.
B) there were a subsidy for the product.
C) production were stopped.
D) the Coase theorem failed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following illustrates the concept of a negative externality?
A) A college professor plays a vigorous game of racquet ball with the racquet he recently purchased.
B) A flood wipes out a farmer's corn crop.
C) A college student plays loud music on his new stereo system at 2:00A.m.
D) A janitor eats a hamburger during his lunch break.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that cookie producers create a positive externality equal to $2 per dozen.What is the relationship between the equilibrium quantity and the socially optimal quantity of cookies to be produced?
A) They are equal.
B) The equilibrium quantity is greater than the socially optimal quantity.
C) The equilibrium quantity is less than the socially optimal quantity.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Coase theorem,private markets will solve externality problems and allocate resources efficiently as long as
A) the externalities that are present are positive, not negative.
B) government assigns property rights to the harmed party.
C) private parties can bargain with sufficiently low transaction costs.
D) businesses determine an appropriate level of production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 10-6
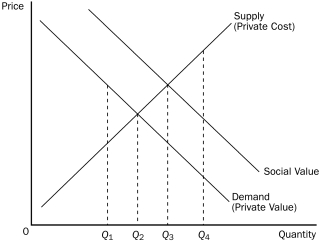 -Refer to Figure 10-6.To internalize the externality in this market,the government should
-Refer to Figure 10-6.To internalize the externality in this market,the government should
A) impose a tax on this product.
B) provide a subsidy for this product.
C) forbid production.
D) produce the product itself.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that large-scale pork production has the potential to create ground water pollution.Why might this type of pollution be considered an externality?
A) The groundwater pollution reduces the cost of large-scale pork production.
B) The economic impact of a large-scale pork production facility is localized in a small geographic area.
C) The pollution has the potential for creating a health risk for water users in the region surrounding the pork production facility.
D) Consumers will not reap the benefits of lower production cost from large-scale pork production.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An externality is
A) the costs that parties incur in the process of agreeing and following through on a bargain.
B) the uncompensated impact of one person's actions on the well-being of a bystander.
C) the proposition that private parties can bargain without cost over the allocation of resources.
D) a market equilibrium tax.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Even if possible,it would be inefficient to prohibit all polluting activity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 288
Related Exams