A) all sharp-spined progeny
B) 50% sharp-spined, 50% dull-spined progeny
C) 25% sharp-spined, 50% dull-spined, 25% spineless progeny
D) It is impossible to determine the phenotypes of the progeny.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A gene for the MN blood group has codominant alleles M and N. If both children in a family are of blood type M, which of the following situations is possible?
A) each parent is either M or MN
B) each parent must be type M
C) both children are heterozygous for this gene
D) neither parent can have the N allele
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of two major forms of neurofibromatosis results from inheriting a dominant allele of a gene with affected individuals having phenotypes that range from mild to very severe. Which of the following is the best explanation for why a young child is the first in her family to be diagnosed with a severe form of the condition?
A) The mother carries the gene but does not express it.
B) One of the parents has a mild expression of the gene.
C) The condition skipped a generation in the family.
D) The child has one more chromosome than either of the parents.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a recessive human disorder in which an individual cannot appropriately break down the amino acid phenylalanine. This amino acid is not naturally produced by humans. Which of the following treatments would be most effective for people with PKU?
A) Feed the individual the substrate that can be metabolized into phenylalanine.
B) Regulate the individual's diet to severely limit the uptake of phenylalanine.
C) Feed the individual the missing enzymes in a regular cycle, such as twice per week.
D) Feed the individual an excess of the missing product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many unique gametes could be produced through independent assortment by an individual with the genotype AaBbCCDdEE?
A) 4
B) 8
C) 16
D) 64
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes how an individual with genotype AaBbCCDdEE can make haploid gametes with different genotypes?
A) mutations during meiosis form new alleles that are incorporated into the gametes
B) crossing over during prophase I leads to increased genetic diversity
C) the inheritance of a particular copy of one chromosome does not affect the inheritance of a different chromosome
D) dominant alleles tend to be inherited together
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Skin color in a certain species of fish is inherited via a single gene with four different alleles. Each allele confers a unit of color darkness such that having allele S1 confers one unit of color, S2 has two units, S3 has three units, and S4 confers four units. A fish of this type has the genotype S1S3, and its mate has the genotype S2S4. What proportion of their offspring would be expected to have five units of color?
A) 1/4
B) 1/8
C) 1/2
D) 0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Phenylketonuria is an inherited disease caused by a recessive allele. If a woman and her husband are both carriers, what is the probability that their first child will be a girl without phenylketonuria?
A) 1/4
B) 3/16
C) 3/8
D) 3/4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In some parts of Africa, the frequency of individuals who are heterozygous for the sickle-cell anemia allele is higher than the frequency in North America, presumably because this reduces the frequency of malaria. Such a relationship is related to which of the following?
A) Mendel's law of independent assortment
B) Mendel's law of segregation
C) Darwin's theory of natural selection
D) Punnett square's modelling inheritance
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A diploid animal is dihybrid at the Head shape (H) and Tail length (T) loci. Which of the following gamete genotypes can it produce?
A) Hh
B) HhTt
C) HHTT
D) Ht
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mendel crossed true breeding yellow-seeded and green-seeded pea plants and then allowed the offspring to self-pollinate to produce an F2 generation. The results were as follows: 6,022 yellow and 2,001 green (8,023 total) . Which of the following statements correctly describes the relationship of the allele for green seeds to the allele for yellow seeds?
A) The green allele is dominant to the yellow allele.
B) The two alleles exhibit incomplete dominance.
C) The green allele is recessive to the yellow allele.
D) The two alleles are codominant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why did all of the F1 offspring of Mendel's purple and white flowered pea cross always look like one of the two parental varieties?
A) No genes interacted to produce a new unique phenotype.
B) Each allele affected phenotypic expression.
C) The traits blended together during fertilization.
D) One allele was dominant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes the terms monohybrid cross and dihybrid cross?
A) A monohybrid cross involves a single parent, whereas a dihybrid cross involves two parents.
B) A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters that are being studied, and a monohybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for only one character being studied.
C) A monohybrid cross is performed for one generation, whereas a dihybrid cross is performed for two generations.
D) A monohybrid cross results in a 9:3:3:1 ratio, whereas a dihybrid cross gives a 3:1 ratio.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In rabbits, the homozygous genotype LCLC has straight legs, LCLc results in deformed legs, and LcLc results in very short legs. The genotype FBFB produces black fur, FBFb brown fur, and FbFb white fur. If a cross is made between brown rabbits with deformed legs and white rabbits with deformed legs, what percent of the offspring would be expected to have deformed legs and white fur?
A) 25%
B) 33%
C) 50%
D) 100%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes how an individual with genotype AaBbCCDdEE can make gametes with eight different genotypes.
A) mutations during meiosis form new alleles that are incorporated into the gametes
B) crossing over during prophase I leads to increased genetic diversity
C) the inheritance of a particular copy of one chromosome does not affect the inheritance of a different chromosome
D) dominant alleles tend to be inherited together
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following question refers to the figure of a family's pedigree chart, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W. Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle. 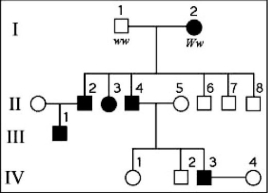 What is the likelihood that a future child of IV-3 and IV-4 will have the trait?
What is the likelihood that a future child of IV-3 and IV-4 will have the trait?
A) 0%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the parent or offspring genotypes or phenotypes are known, the pattern of inheritance can be predicted. Two organisms, with genotypes BbDD and BBDd, are mated. Assuming independent assortment of the two loci, which of the following genotypic ratios in offspring would occur?
A) 1 BBDD: 1 bbdd
B) 1BBDD: 1 BbDD: 1 BBDd: 1 BbDd
C) 9 BBDD: 3 BbDD: 3 BBDd: 1 bbdd
D) 1 BBDD: 2 BbDd: 1bbdd
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following phenotypes is an example of polygenic inheritance?
A) pink flowers in snapdragons
B) the ABO blood group in humans
C) white and purple flower color in peas
D) skin pigmentation in humans
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a particular plant, green seed color is dominant to blue. If two plants with green seeds were crossed and resulted in 302 green and 98 blue seed plants, what was the most probable genotype of each parent?
A) G × G
B) Gg × Gg
C) GG × Gg
D) gg × Gg
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the figure and the following description to answer the question.
In a particular plant, leaf color is controlled by gene locus D. Plants with at least one allele D have dark green leaves, and plants with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have light green leaves. A true-breeding, dark-leaved plant is crossed with a light-leaved one, and the F1 offspring is allowed to self-pollinate. The predicted outcome of the F1 cross is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in the figure, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to each box within the square. 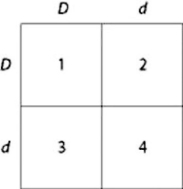 Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to plants that will be true-breeding?
Which of the boxes marked 1-4 correspond to plants that will be true-breeding?
A) 1 and 4 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1, 2, 3, and 4
D) 1 only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 65
Related Exams