A) sucrose
B) an amino acid
C) O2
D) Na+
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects cells that have both CD4 and CCR5 cell surface molecules. The viral nucleic acid molecules are enclosed in a protein capsid, and the protein capsid is itself contained inside an envelope consisting of a lipid bilayer membrane and viral glycoproteins. One hypothesis for viral entry into cells is that binding of HIV membrane glycoproteins to CD4 and CCR5 initiates fusion of the HIV membrane with the plasma membrane, releasing the viral capsid into the cytoplasm. An alternative hypothesis is that HIV gains entry into the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis, and membrane fusion occurs in the endocytotic vesicle. To test these alternative hypotheses for HIV entry, researchers labeled the lipids on the HIV membrane with a red fluorescent dye. 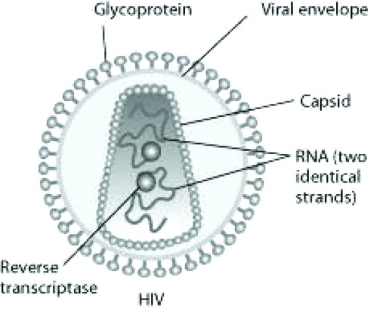 What would be observed by live-cell fluorescence microscopy immediately after HIV entry if HIV enters the cell by endocytosis first, and then later fuses with the endocytotic vesicle membrane?
What would be observed by live-cell fluorescence microscopy immediately after HIV entry if HIV enters the cell by endocytosis first, and then later fuses with the endocytotic vesicle membrane?
A) A spot of red fluorescence will be visible on the infected cell's plasma membrane, marking the site of membrane fusion and HIV entry.
B) The red fluorescent dye-labeled lipids will appear in the infected cell's interior.
C) A spot of red fluorescence will diffuse in the infected cell's cytoplasm.
D) A spot of red fluorescence will remain outside the cell after delivering the viral capsid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure, proteins of the membrane are mostly ________.
A) spread in a continuous layer over the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane
B) confined to the hydrophobic interior of the membrane
C) embedded in a lipid bilayer
D) randomly oriented in the membrane, with no fixed inside-outside polarity
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The voltage across a membrane is called the ________.
A) chemical gradient
B) membrane potential
C) osmotic potential
D) electrochemical gradient
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following cellular processes includes all of the others?
A) osmosis
B) facilitated diffusion
C) passive transport
D) transport of an ion down its electrochemical gradient
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In some cells, there are many different ion electrochemical gradients across the plasma membrane even though there are usually only one or two types of proton pumps present in the membrane. The gradients of the other ions are most likely established by which of the following?
A) cotransport proteins
B) ion channels
C) pores in the plasma membrane
D) passive diffusion across the plasma membrane
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following results is most likely result if a portion of an animal's blood is replaced with distilled water?
A) The animal's red blood cells will shrivel up because the blood has become hypotonic compared to the cells.
B) The animal's red blood cells will swell and possibly burst because the blood has become hypotonic compared to the cells.
C) The animal's red blood cells will shrivel up because the blood has become hypertonic compared to the cells.
D) The animal's red blood cells will burst because the blood has become hypertonic compared to the cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three lab groups carried out an experiment to identify the concentration of sucrose in six solutions. Each unknown solution (1-6) contained one of the following sucrose concentrations: 0.0 M, 0.2 M, 0.4 M, 0.6 M, 0.8 M, and -1.0 M. Cubes of sweet potato (1 cm3) were soaked for 24 hours in each solution and weighed to determine the change in mass. Each data entry represents the average of three sample replicates expressed as percent change in mass following a 24-hour soak in the unknown solutions. From the data provided, which unknown solution has a molarity that most closely reflects the molarity of sweet potato cells?
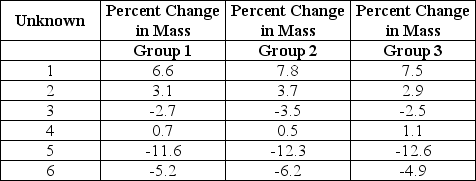
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements most accurately compares primary factors responsible for simple diffusion versus active transport?
A) Simple diffusion is driven by a concentration gradient, while active transport is driven by ADP.
B) Simple diffusion is driven by a concentration gradient, while active transport is driven by ATP hydrolysis.
C) Simple diffusion is driven by ATP hydrolysis, while active transport is driven by an electrochemical gradient.
D) Simple diffusion is driven transmembrane pumps, while active transport is driven by ATP hydrolysis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The force driving simple diffusion is ________, while the energy source for active transport is ________.
A) a concentration gradient; ADP
B) a concentration gradient; ATP hydrolysis
C) transmembrane pumps; an electrochemical gradient
D) phosphorylated carrier proteins; ATP
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
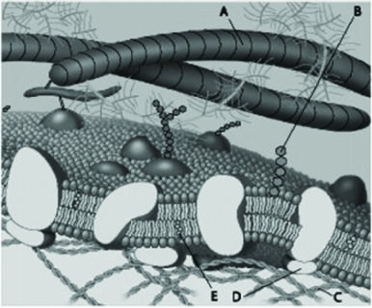 Which component in the figure above is hydrophilic?
Which component in the figure above is hydrophilic?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes is used by white blood cells when engulfing bacteria?
A) phagocytosis
B) pinocytosis
C) osmosis
D) receptor-mediated exocytosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phosphate transport system in bacteria imports phosphate into the cell even when the concentration of phosphate outside the cell is much lower than the cytoplasmic phosphate concentration. Because phosphate import depends on a pH gradient across the membrane, phosphate transport is most likely an example of which of the following transport processes?
A) passive diffusion
B) facilitated diffusion
C) active transport
D) cotransport
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A new drug designed for the treatment of lung cancer must specifically enter the cytoplasm of lung cells while not entering the cells of other tissues. Which of the following characteristics would likely enhance the specificity of this drug?
A) the relative hydrophobicity of the drug molecule
B) the phospholipid composition of lung cell membranes
C) the specificity of the drug molecule for binding to the extracellular matrix of lung cells
D) the similarity of the drug molecule to other molecules normally transported lung cells
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
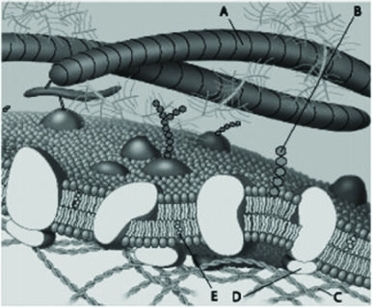 Which component in the figure above represents a protein fiber of the extracellular matrix?
Which component in the figure above represents a protein fiber of the extracellular matrix?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) E
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best explains how the membranes in winter wheat are able to remain fluid in extremely cold temperatures?
A) The membranes contain an increased proportion of unsaturated phospholipids.
B) The membranes contain a reduced proportion of cholesterol molecules.
C) The membranes contain a reduced proportion of hydrophobic proteins.
D) The membranes contain an increased proportion of glycolipids.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes a characteristic feature of diffusion?
A) It is very rapid over long distances.
B) It requires an expenditure of energy by the cell.
C) It is an active process in which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration.
D) It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes a characteristic feature of osmosis?
A) Osmosis only takes place in red blood cells.
B) The process of osmosis requires energy from ATP hydrolysis.
C) In osmosis, water moves across a membrane from areas of lower solute concentration to areas of higher solute concentration.
D) In osmosis, solutes move across a membrane from areas of lower water concentration to areas of higher water concentration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three lab groups carried out an experiment to identify the concentration of sucrose in six solutions. Each unknown solution (1-6) contained one of the following sucrose concentrations: 0.0 M, 0.2 M, 0.4 M, 0.6 M, 0.8 M, and 1.0 M. Cubes of sweet potato (1 cm3) were soaked for 24 hours in each solution and weighed to determine the change in mass. Each data entry represents the average of three sample replicates expressed as percent change in mass following a 24-hour soak in the unknown solutions.
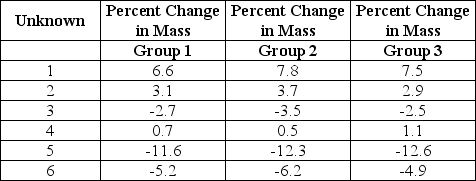 Which unknown solution contains the highest concentration of sucrose?
Which unknown solution contains the highest concentration of sucrose?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 4
D) 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes a characteristic of biological membranes?
A) Phospholipids move laterally within the plane of the membrane.
B) Phospholipids frequently flip-flop from one layer of the membrane to the other.
C) Phospholipids generally occur in an uninterrupted bilayer, with membrane proteins restricted to the surface of the membrane.
D) Phospholipids are arranged with hydrophilic tails in the interior of the membrane.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 67
Related Exams