A) the stroma to the photosystem II.
B) the matrix to the stroma.
C) the stroma to the thylakoid space.
D) the intermembrane space to the matrix.
E) the thylakoid space to the stroma.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In thylakoids, protons travel through ATP synthase from the thylakoid space to the stroma. Therefore, the catalytic "knobs" of ATP synthase would be located
A) on the side facing the thylakoid space.
B) on the ATP molecules themselves.
C) on the pigment molecules of photosystem I and photosystem II.
D) on the stromal side of the membrane.
E) built into the center of the thylakoid stack (granum) .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A gardener is concerned that her greenhouse is getting too hot from too much light, and seeks to shade her plants with colored translucent plastic sheets. What color should she use to reduce overall light energy, but still maximize plant growth?
A) green
B) blue
C) yellow
D) orange
E) any color will work equally well
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are C₄ plants able to photosynthesize with no apparent photorespiration?
A) They do not participate in the Calvin cycle.
B) They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO₂.
C) They are adapted to cold, wet climates.
D) They conserve water more efficiently.
E) They exclude oxygen from their tissues.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the process of carbon fixation, RuBP attaches a CO₂ to produce a six-carbon molecule, which is then split to produce two molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate. After phosphorylation and reduction produces glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) , what more needs to happen to complete the Calvin cycle?
A) addition of a pair of electrons from NADPH
B) inactivation of RuBP carboxylase enzyme
C) regeneration of ATP from ADP
D) regeneration of RuBP
E) regeneration of NADP⁺
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
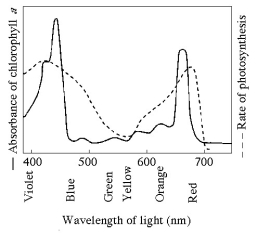 Figure 10.1
-Figure 10.1 shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis. Why are they different?
Figure 10.1
-Figure 10.1 shows the absorption spectrum for chlorophyll a and the action spectrum for photosynthesis. Why are they different?
A) Green and yellow wavelengths inhibit the absorption of red and blue wavelengths.
B) Bright sunlight destroys photosynthetic pigments.
C) Oxygen given off during photosynthesis interferes with the absorption of light.
D) Other pigments absorb light in addition to chlorophyll a.
E) Aerobic bacteria take up oxygen, which changes the measurement of the rate of photosynthesis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume a thylakoid is somehow punctured so that the interior of the thylakoid is no longer separated from the stroma. This damage will have the most direct effect on which of the following processes?
A) the splitting of water
B) the absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
C) the flow of electrons from photosystem II to photosystem I
D) the synthesis of ATP
E) the reduction of NADP⁺
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The splitting of carbon dioxide to form oxygen gas and carbon compounds occurs during
A) photosynthesis.
B) respiration.
C) both photosynthesis and respiration.
D) neither photosynthesis nor respiration.
E) photorespiration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a plant leaf, the reactions that produce NADH occur in
A) the light reactions alone.
B) the Calvin cycle alone.
C) both the light reactions and the Calvin cycle.
D) neither the light reactions nor the Calvin cycle.
E) the chloroplast, but is not part of photosynthesis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In an experiment studying photosynthesis performed during the day, you provide a plant with radioactive carbon (¹⁴C) dioxide as a metabolic tracer. The ¹⁴C is incorporated first into oxaloacetate. The plant is best characterized as a
A) C₄ plant.
B) C₃ plant.
C) CAM plant.
D) heterotroph.
E) chemoautotroph.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reactions that produce molecular oxygen (O₂) take place in
A) the light reactions alone.
B) the Calvin cycle alone.
C) both the light reactions and the Calvin cycle.
D) neither the light reactions nor the Calvin cycle.
E) the chloroplast, but are not part of photosynthesis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to C₃ plants, C₄ plants
A) can continue to fix CO₂ even at relatively low CO₂ concentrations and high oxygen concentrations.
B) have higher rates of photorespiration.
C) do not use rubisco for carbon fixation.
D) grow better under cool, moist conditions.
E) make a four-carbon compound, oxaloacetate, which is then delivered to the citric acid cycle in mitochondria.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In photosynthetic cells, synthesis of ATP by the chemiosmotic mechanism occurs during
A) photosynthesis only.
B) respiration only.
C) both photosynthesis and respiration.
D) neither photosynthesis nor respiration.
E) photorespiration only.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the power fails and the lights go dark, what will happen to CO₂ levels?
A) CO₂ will rise as a result of both animal and plant respiration.
B) CO₂ will rise as a result of animal respiration only.
C) CO₂ will remain balanced because plants will continue to fix CO₂ in the dark.
D) CO₂ will fall because plants will increase CO₂ fixation.
E) CO₂ will fall because plants will cease to respire in the dark.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In C₃ photosynthesis, the reactions that require ATP take place in
A) the light reactions alone.
B) the Calvin cycle alone.
C) both the light reactions and the Calvin cycle.
D) neither the light reactions nor the Calvin cycle.
E) the chloroplast, but is not part of photosynthesis.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?
A) stroma of the chloroplast
B) thylakoid membrane
C) cytoplasm surrounding the chloroplast
D) interior of the thylakoid (thylakoid space)
E) outer membrane of the chloroplast
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement describes the functioning of photosystem II?
A) Light energy excites electrons in the thylakoid membrane electron transport chain.
B) Photons are passed along to a reaction-center chlorophyll.
C) The P680 chlorophyll donates a pair of protons to NADP⁺, which is thus converted to NADPH.
D) The electron vacancies in P680⁺ are filled by electrons derived from water.
E) The splitting of water yields molecular carbon dioxide as a by-product.
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is a correct distinction between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
A) Only heterotrophs require chemical compounds from the environment.
B) Cellular respiration is unique to heterotrophs.
C) Only heterotrophs have mitochondria.
D) Autotrophs, but not heterotrophs, can nourish themselves beginning with CO₂ and other nutrients that are inorganic.
E) Only heterotrophs require oxygen.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In mechanism, photophosphorylation is most similar to
A) substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis.
B) oxidative phosphorylation in cellular respiration.
C) the Calvin cycle.
D) carbon fixation.
E) reduction of NADP⁺.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Plants photosynthesize only in the light. Plants respire
A) in the dark only.
B) in the light only.
C) both in light and dark.
D) never-they get their ATP from photophosphorylation.
E) only when excessive light energy induces photorespiration.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 81
Related Exams