A) 6.02 × 10²³
B) 3.01 × 10²³
C) 6.02 × 10²⁴
D) 12.04 × 10²³
E) 6.02 × 10²²
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Water molecules are able to form hydrogen bonds with
A) compounds that have polar covalent bonds.
B) oils.
C) oxygen gas (O₂) molecules.
D) chloride ions.
E) any compound that is not soluble in water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
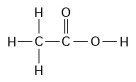 -How many grams of the compound in the figure above would be required to make 1 L of a 0.5 M solution?
(carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
-How many grams of the compound in the figure above would be required to make 1 L of a 0.5 M solution?
(carbon = 12, oxygen = 16, hydrogen = 1)
A) 29
B) 30
C) 60
D) 150
E) 342
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A dietary Calorie equals 1 kilocalorie. Which of the following statements correctly defines 1 kilocalorie?
A) 1,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 1,000°C
B) 100 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 100 g of water by 1°C
C) 10,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°F
D) 1,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of water by 1°C
E) 1,000 calories, or the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 100 g of water by 100°C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molar mass of glucose is 180 g/mol. Which of the following procedures should you carry out to make a 1 M solution of glucose?
A) Dissolve 1 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
B) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
C) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 180 g of water.
D) Dissolve 180 milligrams (mg) of glucose in 1 L of water.
E) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 0.8 L of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the pH of a solution with a hydroxyl ion [OH⁻] concentration of 10⁻¹² ᴹ?
A) pH 2
B) pH 4
C) pH 10
D) pH 12
E) pH 14
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nutritional information on a cereal box shows that one serving of a dry cereal has 200 kilocalories. If one were to burn one serving of the cereal, the amount of heat given off would be sufficient to raise the temperature of 20 kg of water how many degrees Celsius?
A) 0.2°C
B) 1.0°C
C) 2.0°C
D) 10.0°C
E) 20.0°C
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Measurements show that the pH of a particular lake is 4.0. What is the hydroxide ion concentration of the lake?
A) 10⁻¹⁰ M
B) 10⁻⁴ M
C) 10⁻⁷ M
D) 10⁻¹⁴ ᴹ
E) 10 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The bonds that are broken when water vaporizes are
A) ionic bonds.
B) hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
C) covalent bonds between atoms within water molecules.
D) polar covalent bonds.
E) nonpolar covalent bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a single molecule of water, two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) nonpolar covalent bonds.
C) polar covalent bonds.
D) ionic bonds.
E) van der Waals interactions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is readily soluble in water, according to the equation CO₂ + H₂O ↔ H₂CO₃. Carbonic acid (H₂CO₃) is a weak acid. If CO₂ is bubbled into a beaker containing pure, freshly distilled water, which of the following graphs correctly describes the results?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following effects is produced by the high surface tension of water?
A) Lakes don't freeze solid in winter, despite low temperatures.
B) A water strider can walk across the surface of a small pond.
C) Organisms resist temperature changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
D) Evaporation of sweat from the skin helps to keep people from overheating.
E) Water flows upward from the roots to the leaves in plants.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The molar mass of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is 180 g/mol. Which of the following procedures should you carry out to make a 0.5 M solution of glucose?
A) Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of solution is 1 L.
B) Dissolve 90 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
C) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in a small volume of water, and then add more water until the total volume of the solution is 1 L.
D) Dissolve 0.5 g of glucose in 1 L of water.
E) Dissolve 180 g of glucose in 0.5 L of water.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How many molecules of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆ molecular mass = 180 daltons) would be present in 90 grams of glucose?
A) 90 × 10²³
B) (6.02/180) × 10²³
C) (6.02/90) × 10²³
D) (90 x 6.02) × 10²³
E) (90/180) × 6.02 × 10²³
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One liter of a solution of pH 2 has how many more hydrogen ions (H⁺) than 1L of a solution of pH 6?
A) 4 times more
B) 16 times more
C) 40,000 times more
D) 10,000 times more
E) 100,000 times more
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A small birthday candle is weighed, then lighted and placed beneath a metal can containing 100 mL of water. Careful records are kept as the temperature of the water rises. Data from this experiment are shown on the graph. What amount of heat energy is released in the burning of candle wax?
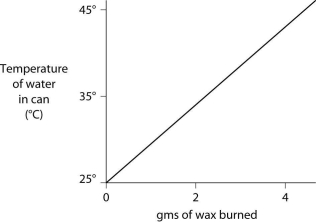
A) 0.5 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
B) 5 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
C) 10 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
D) 20 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
E) 50 kilocalories per gram of wax burned
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the pH of a solution is decreased from 9 to 8, it means that the
A) concentration of H⁺ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what it was at pH 9.
B) concentration of H⁺ has increased tenfold (10X) compared to what it was at pH 9.
C) concentration of OH⁻ has increased tenfold (10X) compared to what it was at pH 9.
D) concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what it was at pH 9.
E) concentration of H⁺ has increased tenfold (10X) and the concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what they were at pH 9.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When an ionic compound such as sodium chloride (NaCl) is placed in water, the component atoms of the NaCl crystal dissociate into individual sodium ions (Na⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻) . In contrast, the atoms of covalently bonded molecules (e.g., glucose, sucrose, glycerol) do not generally dissociate when placed in aqueous solution. Which of the following solutions would be expected to contain the greatest number of solute particles (molecules or ions) ?
A) 1 L of 0.5 M NaCl
B) 1 L of 0.5 M glucose
C) 1 L of 1.0 M NaCl
D) 1 L of 1.0 M glucose
E) 1 L of 1.0 M NaCl and 1 L of 1.0 M glucose will contain equal numbers of solute particles.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A given solution contains 0.0001(10⁻⁴) moles of hydrogen ions [H⁺] per liter. Which of the following best describes this solution?
A) acidic: will accept H⁺ from both strong and weak acids
B) basic: will accept H⁺ from both strong and weak acids
C) acidic: will give H⁺ to weak acids, but accept H⁺ from strong acids
D) basic: will give H⁺ to weak acids, but accept H⁺ from weak acids
E) acidic: will give H⁺ to both strong and weak acids
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following takes place as an ice cube cools a drink?
A) Molecular collisions in the drink increase.
B) Kinetic energy in the drink decreases.
C) A calorie of heat energy is transferred from the ice to the water of the drink.
D) The specific heat of the water in the drink decreases.
E) Evaporation of the water in the drink increases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 70
Related Exams