A) prices.
B) production.
C) both production and prices.
D) neither production nor prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A decrease in the expected future income of the United States would likely:
A) shift its AD curve to the left.
B) shift its AD curve to the right.
C) make its AD curve flatter.
D) make its AD curve steeper.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The multiplier effect exists because:
A) production and expenditures are interdependent.
B) when one person increases expenditures, everyone decreases expenditures.
C) production and expenditures are independent.
D) production lowers expenditures.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would shift the aggregate demand curve to the left?
A) An increase in foreign income
B) A depreciation in the value of the country's currency
C) A higher future expected price level
D) A decrease in exports
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the early years of the Reagan administration, some of the presidential advisors argued that tax cuts could reduce inflation because they would give people an incentive to produce more.Critics of this argument believed that tax cuts would increase inflation, not reduce it.The critics were arguing that tax cuts move the:
A) aggregate demand curve to the right with little change in long-run aggregate supply.
B) aggregate demand curve to the left with little change in long-run aggregate supply.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve to the right with little change in aggregate demand.
D) long-run aggregate supply curve to the left with little change in aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the graph shown.A movement from A to B is most likely to be caused by: 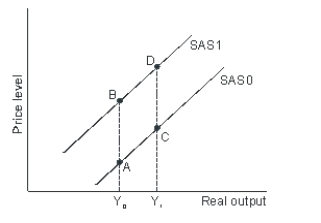
A) an increase in input prices.
B) a decrease in input prices.
C) an increase in aggregate demand.
D) a decrease in aggregate demand.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If productivity and wages both rise by 3 percent, then the aggregate supply curve shifts up.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From 1975 to 1995, the value of the dollar in terms of yen fell from over 300 yen per dollar to about 100 yen per dollar.Considering the impact of this alone, this would likely:
A) shift the U.S.AD curve to the left.
B) shift the U.S.AD curve to the right.
C) make the U.S.AD curve flatter.
D) make the U.S.AD curve steeper.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why would one expect the AD curve to be vertical?
A) If the price level rises, relative prices haven't changed so people would not change their choices.
B) If the price level rises, changes in choices by suppliers are offset by changes in demanders.
C) People do not make choices based on relative prices, but instead based on absolute prices.
D) Substitution is not one of the reasons why the AD curve has its slope.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sharp increase in oil prices along with a decline in labor productivity decline will likely shift the:
A) short-run aggregate supply curve up (to the left) .
B) short-run aggregate supply curve down (to the right) .
C) aggregate demand curve to the right.
D) aggregate demand curve to the left.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The paradox of thrift occurs when:
A) an increase in saving raises output.
B) an increase in saving reduces output.
C) saving is unrelated to output.
D) a decrease in saving reduces output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Starting from a long-run equilibrium, an increase in government expenditures increases output in the short run but not in the long run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the following graph. 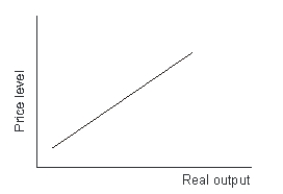 The upward sloping relationship in the diagram represents the:
The upward sloping relationship in the diagram represents the:
A) aggregate demand curve.
B) short-run aggregate supply curve.
C) long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) quantity adjustment curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In the AS/AD model, as the price level falls, the holders of money become richer and buy more.This is one reason why the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most economists agree that it is possible for fiscal policy to fine tune the economy.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the long run, the position of the short-run aggregate supply curve determines:
A) output.
B) the price level.
C) both output and the price level.
D) neither output nor the price level.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a reason why the AD curve slopes downward?
A) International effect
B) Interest rate effect
C) Substitution effect
D) Money wealth effect
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If actual output exceeds potential output, eventually:
A) input prices will rise and output will fall.
B) both input prices and output will rise.
C) input prices will fall and output will rise.
D) both input prices and output will fall.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest rate effect helps to explain why:
A) an increase in the price level reduces the quantity of aggregate demand.
B) an increase in the price level raises investment.
C) a decrease in the price level reduces the quantity of aggregate demand.
D) a decrease in the price level reduces investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As prices fall, the value of people's existing assets rises and people increase expenditures.This occurs as a result of the:
A) international effect.
B) multiplier effect.
C) interest rate effect.
D) money wealth effect.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 163
Related Exams