A) unemployment.
B) inefficiency.
C) less resources.
D) greater entrepreneurship.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2-12 Production possibilities curve 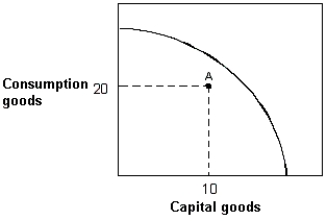 -In Exhibit 2-12, suppose an economy with the given production possibilities curve is currently located at point A in the figure. Which of the following statements is false?
-In Exhibit 2-12, suppose an economy with the given production possibilities curve is currently located at point A in the figure. Which of the following statements is false?
A) This economy could produce more of both capital and consumption goods.
B) This economy is experiencing full employment.
C) This economy could produce more capital goods while holding fixed the number of consumption goods produced.
D) This economy could produce more consumption goods while holding fixed the number of capital goods produced.
E) Not every resource in this economy is being utilized
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about the production possibilities curve when a technological progress occurs? The curve:
A) shifts inwards to the left.
B) becomes flatter at one end and steeper at the other end.
C) becomes steeper.
D) shifts outward to the right.
E) does not change.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2-6 Production possibilities curve data -In Exhibit 2-6, the concept of increasing opportunity costs is represented by the fact that:
A) the quantity of capital goods produced must be less than 150.
B) the quantity of consumer goods is constant for each change in the quantity of capital goods produced.
C) greater amounts of capital goods must be sacrificed to produce each additional unit of consumer goods.
D) the amount of consumer goods produced must be greater than zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correctly lists the three fundamental economic questions?
A) If to produce? Why to produce? When to produce?
B) If to produce? What to produce? How to produce?
C) Why to produce? What to produce? How to produce?
D) What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If some resources were used inefficiently, the economy would operate outside its production possibilities curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2-9 Production possibilities curve 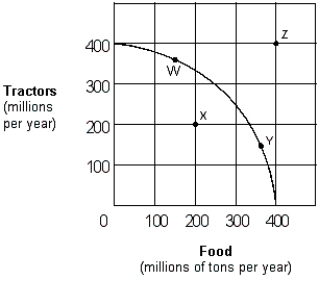 -Movement along this production possibilities curve shown in Exhibit 2-9 indicates:
-Movement along this production possibilities curve shown in Exhibit 2-9 indicates:
A) that labor is not equally productive or homogeneous (nonhomogeneous) .
B) decreasing opportunity costs.
C) all inputs are homogeneous.
D) all of these.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mikki decides to work five hours the night before her economics exam. She earns an extra $75, but her exam score is 10 points lower than it would have been had she stayed home and studied. Her opportunity cost is the:
A) five hours she worked.
B) $75 she earned.
C) 10 points she lost on her exam.
D) time she could have spent watching television.
E) guilt she feels about neglecting her economics studies.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The opportunity cost of watching television is:
A) all of the alternative programs that appear on other stations.
B) zero because there is no money expenditure involved.
C) the alternative use of the time foregone by watching the program.
D) zero if it benefits you.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2-7 Production possibilities curve 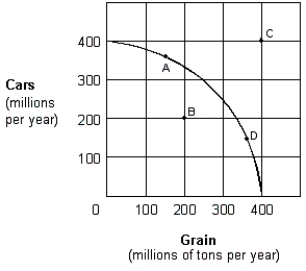 -For the economy shown in Exhibit 2-7, which of the following is true when the economy is at point A?
-For the economy shown in Exhibit 2-7, which of the following is true when the economy is at point A?
A) More cars are being produced than are needed.
B) There must be resources that are not being used fully.
C) Some car production must be forgone in order to produce more grain in the same period.
D) Increased grain production would be impossible.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which fundamental economic question is most closely related to the issues of income distribution and poverty?
A) The What to Produce question.
B) The Why to Produce question.
C) The How to Produce question.
D) The For Whom to Produce question.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In economics, investment refers to the process of accumulating:
A) capital goods.
B) consumer goods.
C) money.
D) stocks and bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would be least likely to cause the production possibilities curve to shift outward?
A) a decreased desire for leisure by workers in the economy.
B) an invention that requires fewer resources to produce a good.
C) a shift in consumer preferences that causes expansion in the output of one product and a decline in output of other products.
D) an expansion in the man-made productive resources available to the economy as the result of a high rate of investment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Assuming an economy is already experiencing full employment, then it must produce more consumer goods and fewer capital goods if it wishes to experience greater rates of economic growth over time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2-13 Production possibilities curve 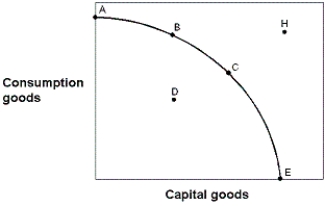 -In Exhibit 2-13, point H is:
-In Exhibit 2-13, point H is:
A) achievable with today's resource base.
B) not achievable today because the economy has not achieved full employment.
C) not achievable today because the economy is not at its maximum point of efficiency.
D) not achievable today because of waste.
E) not achievable today because of inadequate production capacity.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A point outside a production possibilities curve reflects:
A) efficiency.
B) specialization.
C) inefficiency.
D) unemployment.
E) an impossible choice.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 2-18 Production possibilities curves 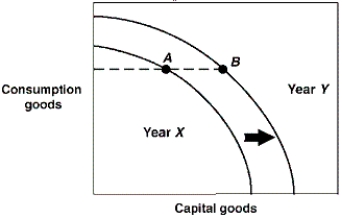 -In Exhibit 2-18, the production possibilities curves for a country are shown for the years Year X and Year Y. Suppose this country was located at point A in Year X and point B in Year Y. This economy:
-In Exhibit 2-18, the production possibilities curves for a country are shown for the years Year X and Year Y. Suppose this country was located at point A in Year X and point B in Year Y. This economy:
A) is worse off in Year Y than in Year X.
B) has stagnated production in this two year period.
C) is more efficient in Year Y than in Year X.
D) has shown growth between these two years.
E) has higher unemployment in Year Y than in Year X.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compare two economies A and B that start out with identical production possibilities curves. Economy A chooses an efficient point with 6 consumption goods and 3 capital goods, while economy B also chooses an efficient point, but with 4 consumption goods and 5 capital goods. In the future we can predict:
A) economy A will operate inefficiently.
B) economy B will operate inefficiently.
C) economy A and economy B will grow equally fast.
D) economy A will grow faster than economy B.
E) economy B will grow faster than economy A.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A rightward (an outward) shift of a nation's production possibilities curve could be caused by:
A) a decrease in technology.
B) an increase in resources.
C) producing more consumer and fewer capital goods.
D) a decline in the labor force's level of education and skills.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One source of economic growth is:
A) producing inside the production possibilities curve.
B) producing outside the production possibilities curve.
C) increasing capital.
D) discouraging profit-seeking entrepreneurs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 202
Related Exams