A) imprinting.
B) a theory of mind.
C) object permanence.
D) a secure attachment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Infants accustomed to a puppet jumping three times on stage show surprise if the puppet jumps only twice. This suggests that Piaget
A) overestimated the continuity of cognitive development.
B) underestimated the cognitive capacities of infants.
C) overestimated the impact of culture on infant intelligence.
D) underestimated the impact of object permanence on infant attachment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Tommy's mother hides his favorite toy under a blanket, he acts as though it no longer exists and makes no attempt to retrieve it. Tommy is clearly near the beginning of Piaget's ________ stage.
A) sensorimotor
B) formal operational
C) concrete operational
D) preoperational
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Studies of monkeys raised with artificial mothers suggest that mother-infant emotional bonds result primarily from mothers providing infants with
A) adequate nourishment.
B) body contact.
C) the opportunity to explore.
D) self-esteem.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lilianne is beginning to develop a fear of strangers and will reach for her mother when she sees someone who is unfamiliar. It is likely that Lilianne has also just
A) mastered the principle of conservation.
B) overcome the limitation of egocentrism.
C) developed a sense of object permanence.
D) lost her sense of secure attachment.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A critical period is a phase during which
A) children frequently disobey and resist their parents.
B) children become able to think hypothetically and reason abstractly.
C) parents frequently show impatience with a child's slowness in becoming toilet trained.
D) exposure to certain experiences is needed for proper development.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Harlows' studies of attachment in monkeys showed that
A) provision of nourishment was the single most important factor motivating attachment.
B) a cloth mother produced the greatest attachment response.
C) whether a cloth or wire mother was present mattered less than the presence or absence of other infants.
D) attachment in monkeys is based on imprinting.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chloe can clearly sense when her sister's teasing is intended to be friendly fun or a hostile put-down. This best illustrates that Chloe has developed a(n)
A) sense of object permanence.
B) insecure attachment.
C) concept of conservation.
D) theory of mind.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Our earliest conscious memories seldom predate our third birthday. This best illustrates
A) egocentrism.
B) imprinting.
C) habituation.
D) infantile amnesia.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Russian psychologist Lev Vygotsky suggested that children's ability to solve problems is enhanced by
A) basic trust.
B) inner speech.
C) conservation.
D) imprinting.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Vygotsky suggested that new words provide a temporary ________ from which children can step to higher levels of thinking
A) preoperational stage
B) neural network
C) critical period
D) scaffold
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One study of 4 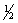 - to 6-year-old children in 10 American cities found that the children's rate of aggressiveness was influenced more by ________ than by the amount of time they spent in day-care programs.
- to 6-year-old children in 10 American cities found that the children's rate of aggressiveness was influenced more by ________ than by the amount of time they spent in day-care programs.
A) children's temperaments
B) parents' caregiving sensitivity
C) family's economic and educational levels
D) all of these factors
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At about 8 months, children become increasingly likely to react to newcomers with tears and distress. This best illustrates
A) role confusion.
B) insecure attachment.
C) egocentrism.
D) stranger anxiety.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to Piaget, children come to understand that the volume of a substance remains constant despite changes in its shape during the ________ stage.
A) sensorimotor
B) preoperational
C) concrete operational
D) formal operational
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Instead of happily exploring the attractive toys located in the pediatrician's waiting room, little Sandra tenaciously clings to her mother's skirt. Sandra most clearly shows signs of
A) habituation.
B) egocentrism.
C) insecure attachment.
D) accommodation.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a British study following over 7000 people from birth to adulthood, those individuals whose fathers were most involved in parenting tended to demonstrate greater
A) role confusion.
B) separation anxiety.
C) egocentrism.
D) academic achievement.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Preschoolers' acquisition of a theory of mind suggests that Piaget overestimated young children's
A) egocentrism.
B) habituation.
C) stranger anxiety.
D) sense of object permanence.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In Piaget's stage of concrete operational intelligence, the child acquires an understanding of the principle of
A) conservation.
B) deduction.
C) attachment.
D) object permanence.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Before Piaget, people were more likely to believe that
A) the child's mind is a miniature model of the adult's.
B) children think about the world in radically different ways from adults.
C) the child's mind develops through a series of stages.
D) children interpret their experiences in terms of their current understandings.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mother who is slow in responding to her infant's cries of distress is most likely to encourage
A) conservation.
B) insecure attachment.
C) object permanence.
D) egocentrism.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 135
Related Exams