A) postsynaptic membrane
B) synaptic cleft
C) synaptic vesicle
D) voltage-gated calcium channel
E) presynaptic terminal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The opening of more and more Na+ ion channels during depolarization
A) is the result of the sodium-potassium exchange pump.
B) is an example of a positive feedback cycle.
C) is possible only if K+ channels remain closed.
D) is the cause of the afterpotential.
E) is an example of a negative feedback cycle.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The plasma membrane of a neuron is more permeable to potassium ions because
A) of its positive electrical charge.
B) there are more leak ion channels for K+ than Na+.
C) protein molecules cannot exit through the cell membrane.
D) calcium ions block Na+ and Cl- channels.
E) there are more leak ion channels for Na+ than K+.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following concerning concentration differences across the plasma membrane. -large molecules trapped inside cell
A) concentration of potassium
B) concentration of sodium and chloride
C) negatively charged proteins
D) sodium/potassium pump
E) plasma membrane is more permeable to this ion because of leak ion channels
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurons in the skin that are responsible for detecting pain are
A) apolar.
B) pseudo-unipolar.
C) bipolar.
D) multipolar.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Gaps or interruptions in the myelin sheath are called
A) internodes.
B) tight junctions.
C) neurofilaments.
D) nodes of Ranvier.
E) gap junctions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The absolute refractory period ends when
A) inactivation gates of voltage-gated Na+ ion channels reopen.
B) activation gates of voltage-gates Na+ ion channels reopen.
C) the sodium-potassium exchange pump stops.
D) voltage-gated K+ channels open.
E) None of these choices is correct.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Arrange the events of synaptic transmission in correct sequence. (1) sodium ions diffuse into the cell and cause a local potential (2) neurotransmitter binds with receptor on postsynaptic cell (3) neurotransmitter diffuses across the synaptic cleft (4) membrane permeability to sodium ions on postsynaptic cell increases (5) action potential causes release of neurotransmitter
A) 5,2,3,4,1
B) 5,2,3,1,4
C) 5,3,4,1,2
D) 5,4,3,2,1
E) 5,3,2,4,1
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mr.Miller has been hospitalized for the flu.The flu virus increases membrane permeability to potassium.You would expect his cells to
A) depolarize.
B) repolarize.
C) isopolarize.
D) hyperpolarize.
E) hypopolarize.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
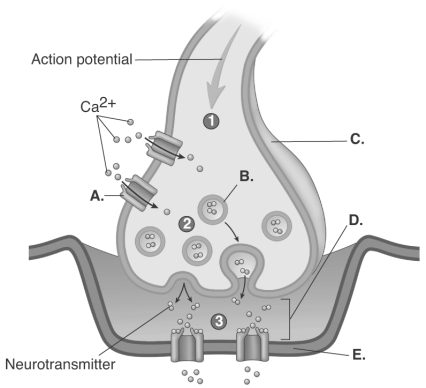 -The figure is a process figure of the chemical synapse.What does "B" represent?
-The figure is a process figure of the chemical synapse.What does "B" represent?
A) postsynaptic membrane
B) synaptic cleft
C) synaptic vesicle
D) voltage-gated calcium channel
E) presynaptic terminal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following concerning concentration differences across the plasma membrane. -requires ATP
A) concentration of potassium
B) concentration of sodium and chloride
C) negatively charged proteins
D) sodium/potassium pump
E) plasma membrane is more permeable to this ion because of leak ion channels
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A neuromodulator
A) acts as a neurotransmitter.
B) inactivates neurotransmitters.
C) is a receptor site for a neurotransmitter.
D) has no influence on the amount of neurotransmitter released.
E) is a substance released from neurons that influences the sensitivity of neurons to neurotransmitters.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
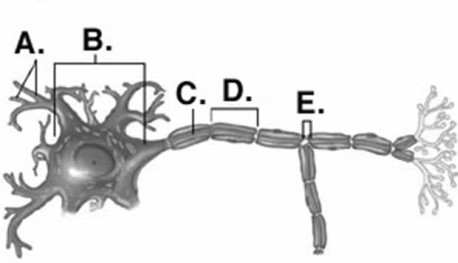 -Identify structure "B" on the neuron.
-Identify structure "B" on the neuron.
A) Schwann cell
B) Node of Ranvier
C) neuron cell body (soma)
D) dendrites
E) axon
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Clusters of gray matter deep within the brain are called
A) cortices.
B) nerves.
C) ganglia.
D) nuclei.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why isn't an action potential transmitted from a postsynaptic membrane to a presynaptic terminal?
A) Presynaptic terminals have no acetylcholine receptors.
B) Presynaptic neurons do not have a resting membrane potential.
C) Acetylcholine can only diffuse in one direction across the synaptic cleft.
D) Synaptic vesicles in the postsynaptic membrane are inactive.
E) Acetylcholine is destroyed too fast.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neurons that have a single axon and a single dendrite are
A) tripolar.
B) bipolar.
C) multipolar.
D) pseudo-unipolar.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the charge difference across the plasma membrane is decreased,
A) the potential difference across the plasma membrane does not change.
B) the membrane potential is more positive.
C) the change is called hyperpolarization.
D) negative proteins can leave the cell.
E) the membrane potential is more negative.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cell bodies of the peripheral nervous system are located in
A) ganglia.
B) Schwann cells.
C) the motor division.
D) the sensory division.
E) nerves.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
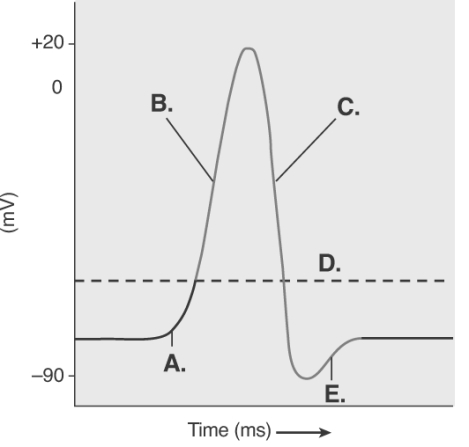 -The figure illustrates the Action Potential.What does "A" represent?
-The figure illustrates the Action Potential.What does "A" represent?
A) repolarization
B) depolarization
C) local potential
D) threshold
E) afterpotential
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The same neurotransmitter binds to a postsynaptic cell but produces a variety of different effects.What does this mean?
A) The postsynaptic cell is expressing different types of receptors for the same neurotransmitter.
B) The strength of the neurotransmitter varies.
C) The amount of neurotransmitter released produces varying effects.
D) The size of the postsynaptic cell makes a difference in neurotransmitter effects.
E) The neuron must be dying.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 155
Related Exams