A) $1,700
B) $1,800
C) $1,900
D) $2,100
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal propensity to save is given by
A) the change in saving divided by the change in consumption.
B) saving divided by the change in disposable personal income.
C) saving divided by disposable income.
D) the change in saving divided by the change in disposable personal income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 13-1 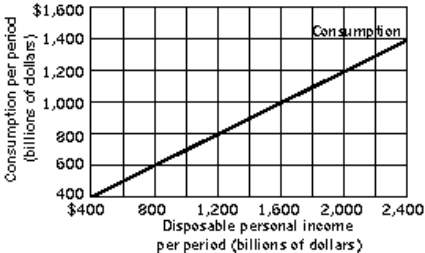 -Refer to Figure 13-1. Assuming that the relationship between consumption and disposable personal income remains linear throughout its entire range, if disposable personal income were zero, what would personal saving be?
-Refer to Figure 13-1. Assuming that the relationship between consumption and disposable personal income remains linear throughout its entire range, if disposable personal income were zero, what would personal saving be?
A) −$200 billion
B) $0
C) $200 billion
D) $400 billion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the permanent income hypothesis,
A) consumption in any period depends on the stable annual income that people expect to earn in their jobs.
B) the amount of income that people require depends on the amount of consumption they need and want to undertake.
C) consumption in any period depends on the average annual income people expect to receive for the rest of their lives.
D) the amount of personal saving depends on the amount of consumption people plan to undertake when they retire.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If consumption is given by C = $10 billion + 0.5Y, and autonomous planned investment, government purchases, and net exports amount to $5 billion, then aggregate expenditures are $20 billion if Y = $10 billion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The interest rate effect suggests that
A) domestic investments fall when foreign interest rates rise relative to domestic interest rates.
B) changes in the price level affect the real purchasing power of money and therefore the money supply.
C) changes in the price level affect the real quantity of money held by households and firms and therefore the interest rate.
D) changes in the price level affect the level of real income and therefore consumption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The multiplier effect indicates that
A) the aggregate demand curve is downward sloping.
B) a change in any autonomous component of aggregate expenditure is buffered by the multiplier effect
C) a change in income causes a magnified change in investment.
D) a change in any autonomous component of aggregate expenditure brings about a magnified change in income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 13-2 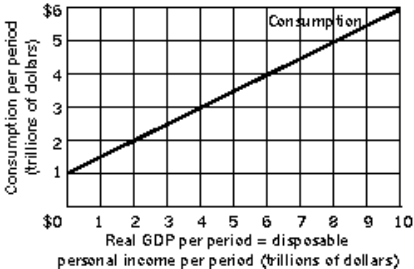 -Refer to Figure 13-2. The marginal propensity to consume equals
-Refer to Figure 13-2. The marginal propensity to consume equals
A) 0.
B) 0.5.
C) 1.0.
D) 2.0.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 13-3 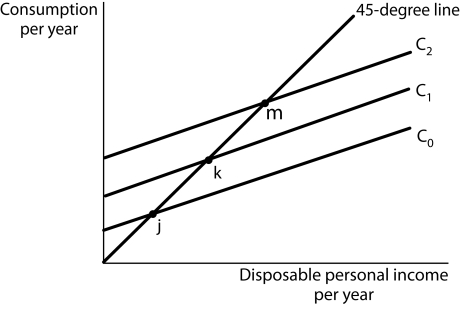 -Refer to Figure 13-3. Suppose the consumption function is given by curve C1. Which of the following will cause a downward shift to curve C1?
-Refer to Figure 13-3. Suppose the consumption function is given by curve C1. Which of the following will cause a downward shift to curve C1?
A) a stock market crash that decreases household wealth
B) a decrease in price level
C) an increase in withholding tax rate
D) rising optimism about economic conditions
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Difficulty: Medium Figure 13-4 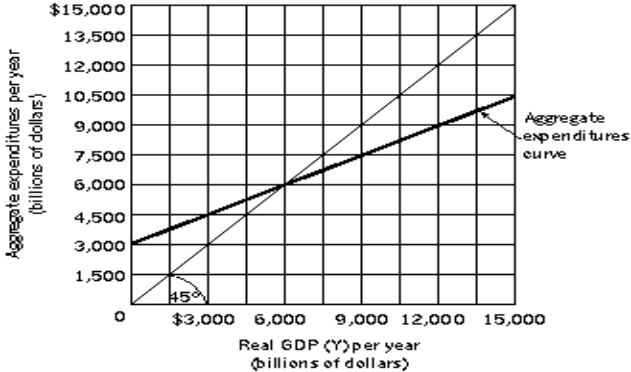 -Refer to Figure 13-4. Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption,
IP = Planned Investment. Suppose AE = C + IP. IP is autonomous and the consumption function is C = $1,000 billion + 0.5Y. If real GDP = $7,000 billion, what is the amount of aggregate expenditures?
-Refer to Figure 13-4. Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption,
IP = Planned Investment. Suppose AE = C + IP. IP is autonomous and the consumption function is C = $1,000 billion + 0.5Y. If real GDP = $7,000 billion, what is the amount of aggregate expenditures?
A) $6,000 billion
B) $6,500 billion
C) $7,000 billion
D) $7,500 billion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 13-6 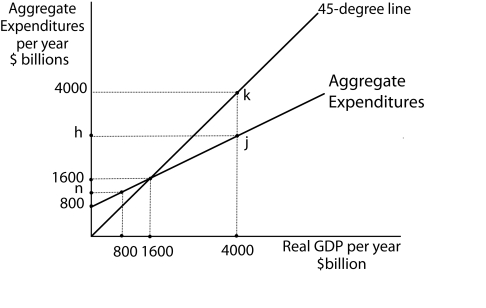 -Refer to Figure 13-6. Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption,
IP = Planned Investment, G = Government Purchases. Further, IP and G are autonomous. If real GDP produced is $4,000, what is the amount of unplanned investment?
-Refer to Figure 13-6. Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption,
IP = Planned Investment, G = Government Purchases. Further, IP and G are autonomous. If real GDP produced is $4,000, what is the amount of unplanned investment?
A) zero
B) $1,200 billion
C) $2,400 billion
D) $2,800 billion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Aggregate expenditures that do not vary with real GDP are called autonomous aggregate expenditures.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose the consumption function is C = $500 + 0.8Y. If Y = $1,000, what is the amount of consumption?
A) $300
B) $500
C) $1,000
D) $1,300
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During an economic downturn, households respond to a decline in income by
A) reducing taxes.
B) reducing consumption.
C) increasing the quantity of labor supplied.
D) negotiating higher wages.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
May has been holding her retirement savings in a safe in her house. If the economy is currently experiencing a falling price level,
A) the real purchasing power of her money remains constant.
B) the real value of her savings is decreasing as long as the price level is falling.
C) the real value of her savings is increasing as long as the price level is falling.
D) the nominal value of her savings remains constant.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the real wealth effect, if you are living in a period of rising price levels, the cost of the goods and services you buy
A) decreases and your real income increases.
B) increases and your real income increases.
C) increases and your real income remains the same.
D) increases and your real income decreases.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An upward shift in the consumption function can be caused by
A) expectations of product shortages.
B) expectations of less income in the future.
C) a decrease in consumer confidence.
D) a reduction in the wealth of households.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 13-5 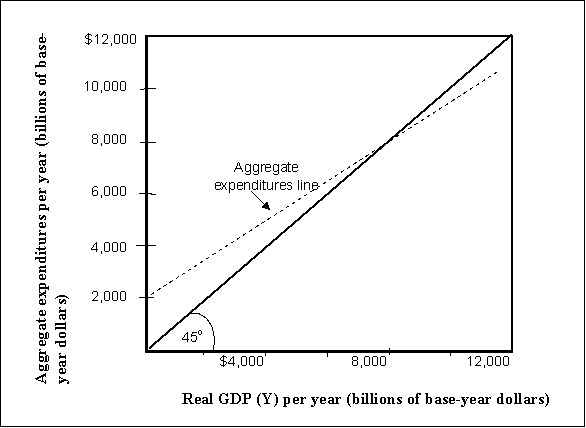 -Refer to Figure 13-5. Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption,
IP = Planned Investment. Consider a simple economy where AE = C + IP, IP is autonomous
And the consumption function is given by C = $1,000 billion + 0.75Y. What is the value of equilibrium real GDP (Y*) ?
-Refer to Figure 13-5. Let Y = real GDP, AE = Aggregate Expenditures, C = Consumption,
IP = Planned Investment. Consider a simple economy where AE = C + IP, IP is autonomous
And the consumption function is given by C = $1,000 billion + 0.75Y. What is the value of equilibrium real GDP (Y*) ?
A) $2,000 billion
B) $6,000 billion
C) $7,500 billion
D) $8,000 billion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal propensity to consume is the
A) slope of the saving function.
B) slope of the consumption-saving curve.
C) slope of the saving-investment curve.
D) change in consumption divided by the change in disposable personal income.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The amount of consumption that would take place if real GDP were zero is called
A) induced consumption.
B) exogenous consumption.
C) autonomous consumption.
D) break even consumption.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 218
Related Exams